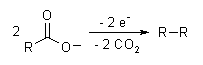Informatics Educational Institutions & Programs
The Kolbe electrolysis or Kolbe reaction is an organic reaction named after Hermann Kolbe.[1] The Kolbe reaction is formally a decarboxylative dimerisation of two carboxylic acids (or carboxylate ions). The overall reaction is:
If a mixture of two different carboxylates are used, all combinations of them are generally seen as the organic product structures:
- 3 R1COO− + 3 R2COO− → R1−R1 + R1−R2 + R2−R2 + 6 CO2 + 6 e−
The reaction mechanism involves a two-stage radical process: electrochemical decarboxylation gives a radical intermediate, which combine to form a covalent bond.[2] As an example, electrolysis of acetic acid yields ethane and carbon dioxide:
- CH3COOH → CH3COO− → CH3COO· → CH3· + CO2
- 2CH3· → CH3CH3
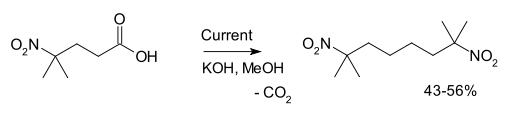
Another example is the synthesis of 2,7-dimethyl-2,7-dinitrooctane from 4-methyl-4-nitrovaleric acid:[3]
See also
References
- ^ Utley, James (1997). "Trends in Organic Electrosynthesis". Chemical Society Reviews. 26 (3): 157. doi:10.1039/cs9972600157.
- ^ Vijh, A. K.; Conway, B. E. (1967). "Electrode Kinetic Aspects of the Kolbe Reaction". Chem Rev. 67 (6): 623–664. doi:10.1021/cr60250a003.
- ^ Sharkey, W. H.; Langkammerer, C. M. (1973). "2,7-Dimethyl-2,7-dinitrooctane". Organic Syntheses; Collected Volumes, vol. 5, p. 445.
Further reading
- Kolbe, Hermann (1848). "Zersetzung der Valeriansäure durch den elektrischen Strom" [Decomposition of valeric acid by an electric current]. Annalen der Chemie und Pharmacie. 64 (3): 339–341. doi:10.1002/jlac.18480640346.
- Kolbe, Hermann (1849). "Untersuchungen über die Elektrolyse organischer Verbindungen" [Investigations of the electrolysis of organic compounds]. Annalen der Chemie und Pharmacie. 69 (3): 257–294. doi:10.1002/jlac.18490690302.
External links
- "Kolbe Electrolysis". Organic Chemistry Portal. Retrieved 22 October 2007.