Informatics Educational Institutions & Programs
Contents
In organic chemistry, a sugar acid or acidic sugar is a monosaccharide with a carboxyl group at one end or both ends of its chain.[1]
Main classes of sugar acids include:
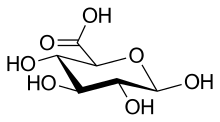
- Aldonic acids, in which the aldehyde group (−CH=O) located at the initial end (position 1) of an aldose is oxidized.
- Ulosonic acids, in which the hydroxymethyl group (−CH2OH) at the initial end of a 2-ketose is oxidized creating an α-ketoacid.
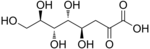
- Uronic acids, in which the −CH2OH group at the terminal end of an aldose or ketose is oxidized.
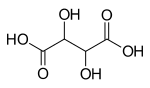
- Aldaric acids, in which both ends (−CH=O and −CH2OH) of an aldose are oxidized.
 |
 |
 |
Examples
Examples of sugar acids include:
- Aldonic acids
- Glyceric acid (3C)
- Xylonic acid (5C)
- Gluconic acid (6C)
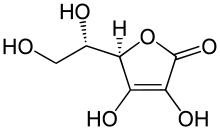
- Ascorbic acid[2] (6C, unsaturated lactone)
- Ulosonic acids
- Neuraminic acid (5-amino-3,5-dideoxy-D-glycero-D-galacto-non-2-ulosonic acid)
- Ketodeoxyoctulosonic acid (KDO or 3-deoxy-D-manno-oct-2-ulosonic acid)
- Uronic acids
- Glucuronic acid (6C)
- Galacturonic acid (6C)
- Iduronic acid (6C)
- Aldaric acids
- Tartaric acid (4C)
- meso-Galactaric acid (Mucic acid) (6C)
- D-Glucaric acid (Saccharic acid) (6C)
 |
 |
References
- ^ Robyt, J.F. (1998). Essentials of carbohydrate chemistry. New York: Springer. ISBN 0-387-94951-8.
- ^ Davies Michael B.; Austin John; Partridge David A. (1991). Vitamin C: Its Chemistry and Biochemistry. The Royal Society of Chemistry. p. 48. ISBN 0-85186-333-7.
External links
- Sugar+Acids at the U.S. National Library of Medicine Medical Subject Headings (MeSH)