Fast SARS-CoV-2 detection by RT-qPCR in preheated nasopharyngeal swab samples
| Full article title | Fast SARS-CoV-2 detection by RT-qPCR in preheated nasopharyngeal swab samples |
|---|---|
| Journal | International Journal of Infectious Diseases |
| Author(s) |
Alcoba-Florez, Julia; González-Montelongo, Rafaela; Íñigo-Campos, Antonio; García-Martínezde Artola, Diego; Gil-Campesino, Helena; The Microbiology Technical Support Team; Ciuffreda, Laura; Valenzuela-Fernández, Agustín; Flores, Carlos |
| Author affiliation(s) |
Hospital Universitario Nuestra Señora de Candelaria, Instituto Tecnológico y de Energías Renovables, Universidad de La Laguna, Instituto de Salud Carlos III |
| Primary contact | Email: cflores at ull dot edu dot es |
| Year published | 2020 |
| Volume and issue | 97 |
| Page(s) | 66–68 |
| DOI | 10.1016/j.ijid.2020.05.099 |
| ISSN | 1201-9712 |
| Distribution license | Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International |
| Website | https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S1201971220304069 |
| Download | https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S1201971220304069/pdfft (PDF) |
Abstract
Objectives: The gold-standard COVID-19 diagnosis relies on detecting SARS-CoV-2 using RNA purification and one-step retrotranscription and quantitative real-time PCR (RT-qPCR). Based on the urgent need for high-throughput screening, we tested the performance of three alternative protocols that are simple and affordable for rapidly detecting SARS-CoV-2, bypassing the long and tedious RNA extraction step and reducing the time to viral detection.
Methods: We evaluated three methods based on direct nasopharyngeal swab viral transmission medium (VTM) heating before RT-qPCR: a) direct without additives; b) in a formamide-EDTA (FAE) buffer, and c) in a RNAsnap buffer.
Results: Although with a delay in cycle threshold compared to the gold-standard, we found consistent results in nasopharyngeal swab samples that were subject to a direct 70°C incubation for 10 minutes.
Conclusions: Our findings provide valuable options to overcome any supply chain issue and help to increase the throughput of diagnostic tests, thereby complementing standard diagnosis.
Keywords: COVID-19, SARS-CoV-2, diagnosis, sample treatment, RNA extraction, fast protocols
Introduction
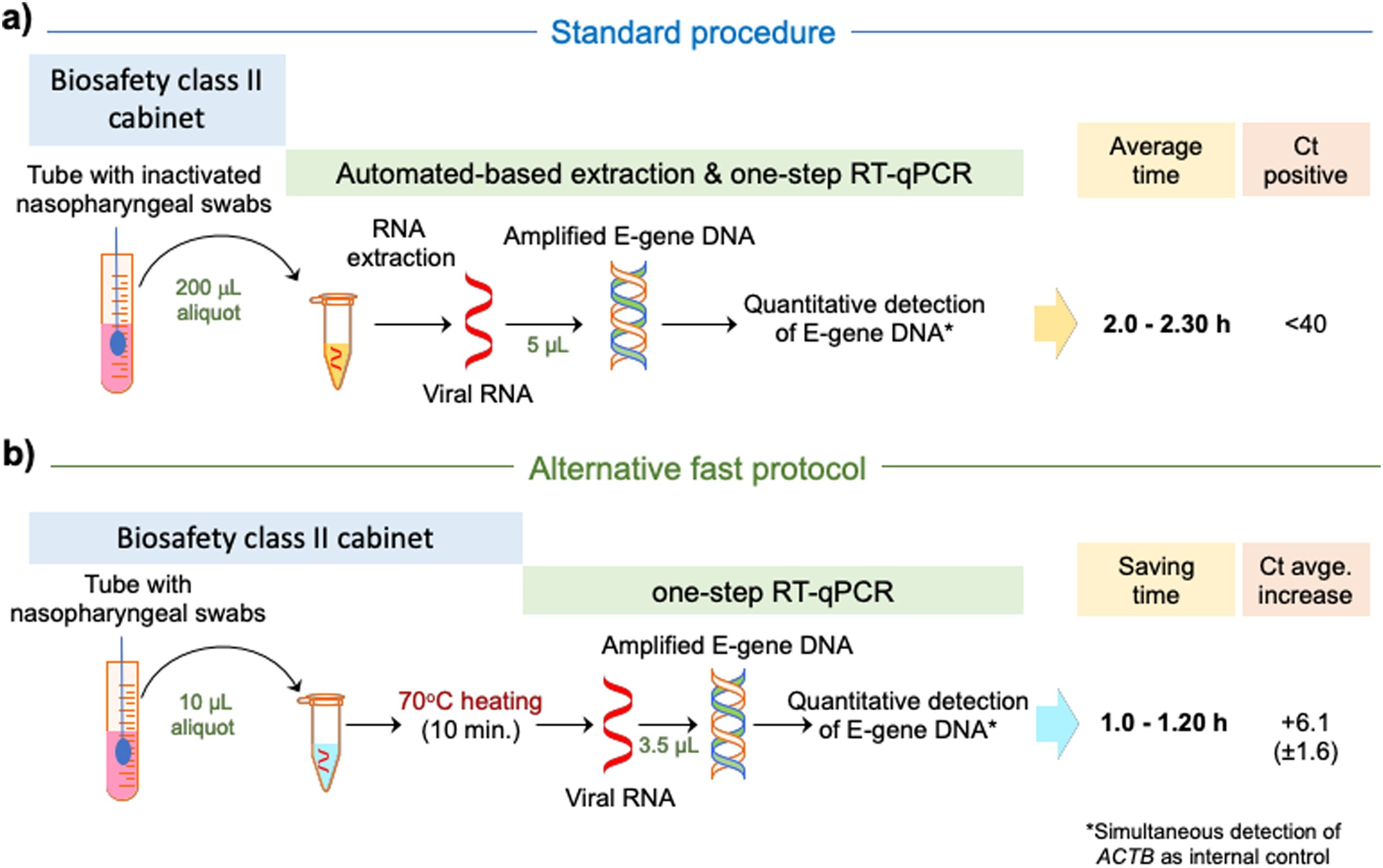
The ongoing coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) worldwide pandemic being caused by the severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) virus (see WHO situation reports for more) has imposed an unexpected high burden on health care systems around the world, leading to an increasing demand for daily diagnostic screening. The current standard assay for diagnosis is based on the extraction of RNA from respiratory samples—especially from nasopharyngeal swab viral transport media (VTM)—and subsequent one-step reverse transcription and real-time quantitative PCR (RT-qPCR) targeting one or several sequences from SARS-CoV-2.[1] However, this standard procedure usually takes from 3.5 to 4.0 hours due to manual interventions. Additionally, there is a risk of reagent shortage in major kit suppliers, particularly for the RNA extraction step. Alternatives to accelerate this procedure have been proposed as a consequence, with the most efficient alternative relying on loop-mediated isothermal amplification (LAMP).[2]
Here we aimed to simplify the current diagnostic standard for COVID-19 by skipping the RNA extraction step. We tested three simple approaches based on direct nasopharyngeal swab VTM heating before the RT-qPCR: a) directly without additives (Direct); b) in a formamide-EDTA (FAE) buffer[3]; and c) in a RNAsnap buffer.[4]
Materials and methods
The study was conducted at the University Hospital Nuestra Señora de Candelaria (Santa Cruz de Tenerife, Spain) during March 2020. For the exploratory stage, we selected nasopharyngeal swabs from four COVID-19 patients and four COVID-19 negative controls. For the validation stage, 90 independent samples (41 SARS-CoV-2 positives and 49 negatives) were subjected to the treatment providing the smallest cycle threshold deviations from the standard protocol in the exploratory stage. Sample manipulation and diagnosis, as well as alternative protocols, are detailed in the supplementary data at the end of this article.
Results
Exploratory stage
The non-template control did not show amplification in any of the protocols both for SARS-CoV-2 or the internal control (Supplementary data, Table S1). The positive control for the E-gene amplification yielded positive results in the RT-qPCR experiments of the three alternative protocols. Furthermore, all samples gave positive results for the internal control. When RT-qPCR was carried out on the same four positive samples treated using the alternative protocols (Direct, FAE, and RNAsnap), we observed amplification of the E-gene in all three conditions, although with a displacement of the cycle threshold (Ct) values (Table 1). Compared to standard RNA extraction, we observed an average (± SD) increase in the Ct of 6.9 (± 1.7), 8.5 (± 1.1), and 7.8 (± 1.7) for the Direct, FAE, and RNAsnap treatments, respectively (Supplementary data, Figure S1).
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Validation stage
Based on these results, we assayed 90 independent VTM samples from 41 COVID-19 positives (Table S2) and 49 negatives using the Direct method. We verified that all samples gave positive results for the internal control (average Ct of 29.6 ± 2.5) although the amplification Ct was, on average, slightly larger than that obtained by the standard RNA extraction method in the same samples (average Ct of 27.0 ± 1.5).
Out of the 41 SARS-CoV-2 positive VTM samples, only five did not yield amplification for the E-gene with the Direct treatment. Regarding the internal control results on the extracted RNA of these five samples, we did not observe significant differences when compared with those from the other SARS-CoV-2 positive samples (average Ct of 27.6 ± 1.2 and 26.9 ± 1.6, respectively; p = 0.457). However, their Ct values for the E-gene were larger (average Ct of 34.0 ± 2.0 and 25.7 ± 4.9, respectively; p = 0.0007). Therefore, we considered these five samples as false negatives, corresponding to a false negative rate in the Direct treatment of 12% (95% confidence interval [CI] = 5-28). Considering the 36 samples that were SARS-CoV-2 positive by the two methods, there was an average increase in the E-gene Ct by the Direct method of 6.1 (± 1.6) compared to that obtained by a standard RNA extraction. None of the SARS-CoV-2 negative VTM samples was classified as positive by the Direct treatment. Therefore, the Direct method yielded a sensitivity, specificity, and accuracy of 87.8% (95% CI = 73.8-95.9), 100% (95% CI = 92.8-100), and 99.9% (95% CI = 95.7-100), respectively.
Discussion
While the three heating treatments of the sample and direct use in the subsequent detection showed positive amplification of the SARS-CoV-2 E-gene, the Direct method provided the best results, which were highly consistent with the SARS-CoV-2 infection diagnosis based on standard RNA extraction (Fig. 1a), while performed in nearly half of the time (Fig. 1b). We caution that the study was done with a limited number of samples, and amplifications should be closely monitored to avoid increasing the false negatives above that of the standard diagnosis based on RNA extractions.[5] Despite that, diverse empirical assessments of our protocol and that proposed by Fomsgaard and Rosenstierne[6] revealed that the quantitative results are highly comparable.[7] Remarkably, SARS-CoV-2 and SARS-CoV-1 show comparable environmental stability[8], and evidence suggests that SARS-CoV-1[9] and SARS-CoV-2[10] lose infectivity above 56 °C within short periods of time, and without any significant effect on the number of viral gene-copies detected by RT-qPCR below 92 °C, even after 30 to 60 minutes of pre-treatment.[10] Therefore, we postulate that the Direct protocol at 70 °C for 10 minutes may also help to diminish the infectiveness of the samples, without significant viral RNA degradation during manipulation.
|
Finally, we warn that the choice of RT-qPCR kits might have an impact on the sensitivity of the Direct protocol. For example, the average increase in the Ct by the Direct method compared to the standard RNA extraction was 3.5 (± 2.0) using the newly released TaqPath COVID-19 CE-IVD RT-PCR Kit using their ORF1ab assay (Thermo Fisher Scientific).
Supplementary data
The following is supplementary data to this article: Word document, 44kb
Acknowledgements
We offer many thanks to the University Hospital Nuestra Señora de Candelaria board of directors and the executive team for their strong support and assistance in accessing the diverse resources used in the study.
Authors’ contributions
JAF, RGM and CF designed the study. JAF, RGM, AIC, DGM, HGC, TMTST, and CF participated in data acquisition. JAF, RGM, and CF performed the analyses and data interpretation. LC, AVF, RGM, and CF wrote the draft of the manuscript. All authors contributed in the critical revision and final approval of the manuscript.
The Microbiology Technical Support Team
M. Sonia Batista-Torres, Concepción Beltrán-Tacoronte, Esther G. Gómez-Ruíz, Victoria González-González, Teodora Manrique-Izquierdo, Rocío M. Rivera-Ruiz, Iru Trujillo-Medina, Guacimara Espinel- Guerra, Chaxiraxi Medina-Coello, and M. Candelaria Padilla-Martín
Funding
This research was funded by Cabildo Insular de Tenerife, [grant number CGIEU0000219140]; the agreement with Instituto Tecnológico y de Energías Renovables (ITER) to strengthen scientific and technological education, training research, development and innovation in Genomics, Personalized Medicine and Biotechnology, [grant number OA17/008]; Ministerio de Innovación y Ciencia, [grant number RTI2018-093747-B-100 and RTC-2017-6471-1], co-funded by the European Regional Development Fund (ERDF); Lab P2+ facility, [grant number UNLL10-3E-783], co-funded by the ERDF and “Fundación CajaCanarias”; and the Spanish HIV/AIDS Research Network, [grant number RIS-RETIC, RD16/0025/0011], co-funded by Instituto de Salud Carlos III and by the ERDF.
Ethical approval
The University Hospital Nuestra Señora de Candelaria (Santa Cruz de Tenerife, Spain) review board approved the study (ethics approval number: CHUNSC_2020_24).
Conflicts of interest
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
References
- ↑ Corman, V.M.; Landt, O.; Kaiser, M. et al. (2020). "Detection of 2019 Novel Coronavirus (2019-nCoV) by Real-Time RT-PCR". Euro Suveillance 25 (3): 2000045. doi:10.2807/1560-7917.ES.2020.25.3.2000045. PMC PMC6988269. PMID 31992387. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6988269.
- ↑ Esbin, M.N.; Whitney, O.N.; Chong, S. et al. (2020). "Overcoming the Bottleneck to Widespread Testing: A Rapid Review of Nucleic Acid Testing Approaches for COVID-19 Detection". RNA 26 (7): 771-783. doi:10.1261/rna.076232.120. PMC PMC7297120. PMID 32358057. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC7297120.
- ↑ Shedlovskiy, D.; Shcherbik, N.; Pestov, D.G. (2017). "One-step Hot Formamide Extraction of RNA From Saccharomyces Cerevisiae". RNA Biology 14 (12): 1722-1726. doi:10.1080/15476286.2017.1345417. PMC PMC5731811. PMID 28692404. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5731811.
- ↑ Stead, M.B.; Agrawal, A.; Bowden, K.E. et al. (2012). "RNAsnap™: A Rapid, Quantitative and Inexpensive, Method for Isolating Total RNA From Bacteria". Nucleic Acids Research 40 (20): e156. doi:10.1093/nar/gks680. PMC PMC3488207. PMID 22821568. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3488207.
- ↑ Xie, X.; Zhong, Z.; Zhao, W. et al. (2020). "Chest CT for Typical 2019-nCoV Pneumonia: Relationship to Negative RT-PCR Testing". Radiology: 200343. doi:10.1148/radiol.2020200343. PMC PMC7233363. PMID 32049601. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC7233363.
- ↑ Fomsgaard, A.S.; Rosenstierne, M.W. (2020). "An Alternative Workflow for Molecular Detection of SARS-CoV-2 - Escape From the NA Extraction Kit-Shortage, Copenhagen, Denmark, March 2020". Euro Surveillance 25 (14): 2000398. doi:10.2807/1560-7917.ES.2020.25.14.2000398. PMC PMC7160440. PMID 32290902. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC7160440.
- ↑ Calvez, R.M.M.; Taylor, A.; Calvo=Bado, L. et al. (2020). "Molecular detection of SARS-CoV-2 using a reagent-free approach". medRxiv. doi:10.1101/2020.04.28.20083626.
- ↑ van Doremalen, N.; Bushmaker, T.; Morris, D.H. et al. (2020). "Aerosol and Surface Stability of SARS-CoV-2 as Compared With SARS-CoV-1". New England Journal of Medicine 382 (16): 1564-1567. doi:10.1056/NEJMc2004973. PMC PMC7121658. PMID 32182409. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC7121658.
- ↑ Geller, C.; Varbanov, M.; Duval, R.E. (2012). "Human Coronaviruses: Insights Into Environmental Resistance and Its Influence on the Development of New Antiseptic Strategies". Viruses 4 (11): 3044-68. doi:10.3390/v4113044. PMC PMC3509683. PMID 23202515. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3509683.
- ↑ 10.0 10.1 Pastorino, B.; Touret, F.; Gilles, M. et al. (2020). "Evaluation of heating and chemical protocols for inactivating SARS-CoV-2". bioRxiv. doi:10.1101/2020.04.11.036855.
Notes
This presentation is faithful to the original, with only a few minor changes to presentation, spelling, and grammar. In some cases important information was missing from the references, and that information was added. References in this version are listed in order of appearance—by design—rather than alphabetical order as the original was. Otherwise, no other changes were made in conformance with the "NoDerivatives" portion of the document license.