Posted on December 20, 2016
By John Jones
Journal articles

In this short paper, Williams
et al. of the University of Michigan provide a brief technical view of microservices and how they have the potential to improve the organization and use of bioinformatics and other healthcare applications. They propose that "a well-established software design and deployment strategy" that uses micorservices framework can improve the collaborative and patient-focused efforts of researchers and laboratorians everywhere. They conclude that bioinformaticians, pathologists, and other laboratorians "can contain ever-expanding IT costs, reduce the likelihood of IT implementation mishaps and failures, and perhaps most importantly, greatly elevate the level of service" with properly implemented microservice-based versions of the software they use.
Posted on December 12, 2016
By John Jones
Journal articles
In this brief paper published in 2016, Wolske and Rhinesmith present what they call "a set of critical questions" for guiding those delving into a community informatics (CI) project. Properly using technology that allows collaboration, popular education, and asset development tools, community informatics projects are able to carry on with the primary goal of sustainably supporting community development projects. However, the authors argue, a set of ethical questions should be asked to drive the planning, development, and implementation of said CI projects. These questions, presented in this paper, have the potential to better "guide the evolution of ethical community informatics in practice, as well as the personal transformation of CI practitioners who seek to embrace all as equals and experts."
Posted on December 7, 2016
By John Jones
Journal articles
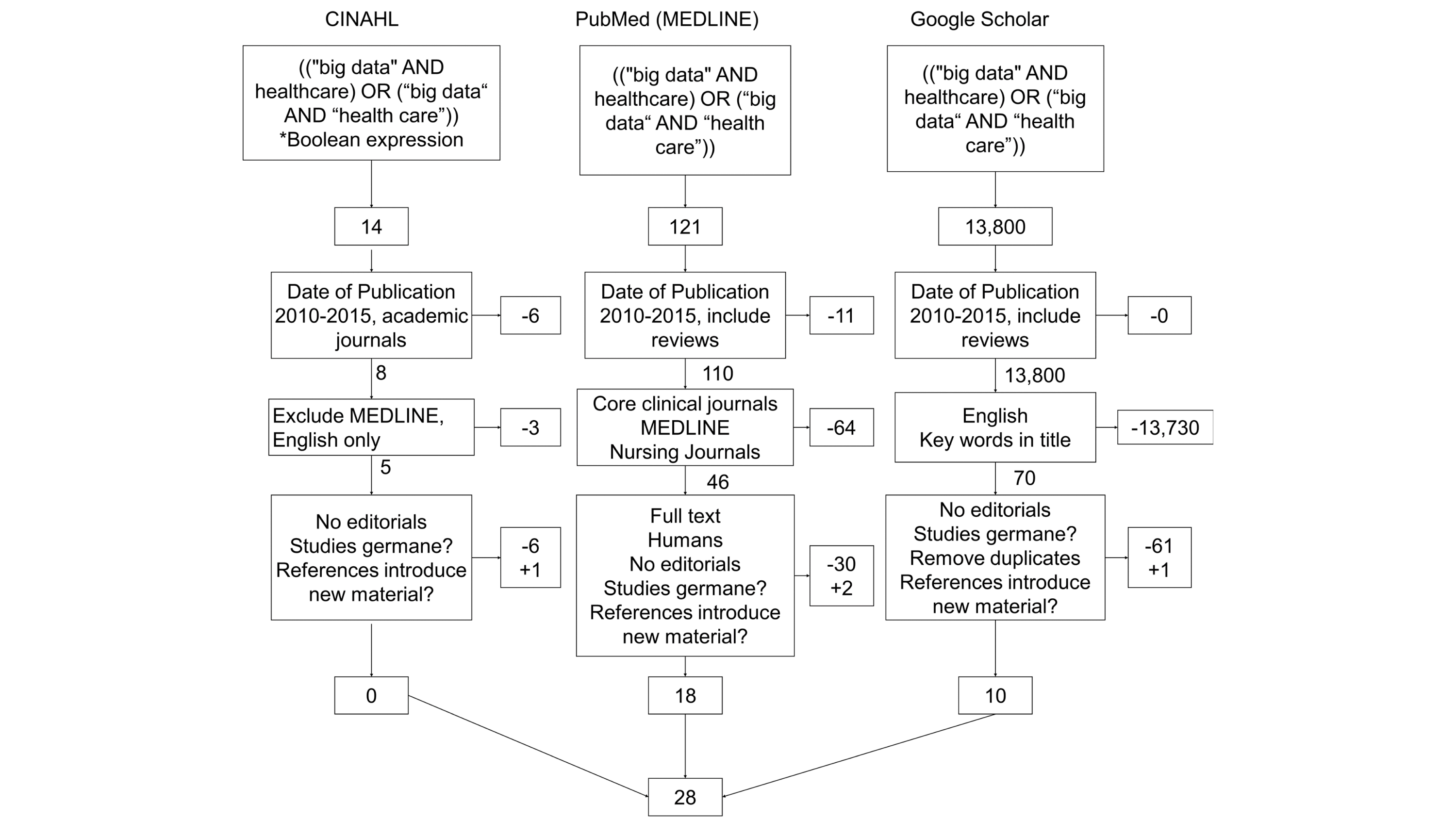
In this 2016 article published in
JMIR Medical Informatics, Kruse
et al. of the Texas State University present the results of a systematic review of articles and studies involving big data in the health care sphere. From this review the team identified nine challenges and 11 opportunities that big data brings to health care. The group describes these challenges and opportunities, concluding that either way "the vast amounts of information generated annually within health care must be organized and compartmentalized to enable universal accessibility and transparency between health care organizations."
Posted on November 28, 2016
By John Jones
Journal articles

Moving data between systems via an electronic exchange (interoperability) while keeping it clean is always a challenge. Data exchanged between electronic health records (EHR) and immunization information system (IIS) is no exception, as Woinarowicz and Howell demonstrate in this 2016 paper published in
Online Journal of Public Health Informatics. Working for the North Dakota Department of Health, Division of Disease Control, the duo explain how setting up their IIS for interoperability with provider EHRs "has had an impact on NDIIS data quality." They conclude: "Timeliness of data entry has improved and overall doses administered have remained fairly consistent, as have the immunization rates ... [but more] will need to be done by NDIIS staff and its vendor to help reduce the negative impact of duplicate record creation, as well as data completeness."
Posted on November 21, 2016
By John Jones
Journal articles
Genomic data is increasingly used to provide better, more focused clinical care. Or course, its associated datasets can be large, and it can take significant processing power to utilize and manage effectively. In this 2016 paper published in
Journal of Personalized Medicine, Tsai
et al. of Partners Healthcare describe their "bioinformatics strategy to efficiently process and deliver genomic data to geneticists for clinical interpretation." They conclude that with more research comes improved workflows and "filtrations that include larger portions of the non-coding regions as they start to have utility in the clinical setting, ultimately enabling the full utility of complete genome sequencing."
Posted on November 16, 2016
By John Jones
Journal articles
Synoptic reporting is an important part of not only managing patient testing information but also reporting that data for research and data mining purposes. As such, the extraction of particular elements from these types of reports — including those recording major cancer information — has historically been difficult. Recent developments in extracting key information from synoptic reports have made it easier, however, including the use of the R programming language. In this paper by J.J. Ye, the process of extracting melanoma data from pathology datasets is used to describe a broader, wide-ranging application of R and the associated RODBC package for extracting useful data from synoptic reports. Ye concludes: "This approach can be easily modified and adopted for other pathology information systems that use relational database for data management."
Posted on November 10, 2016
By John Jones
Journal articles

In this 2016 paper published in
Data Science Journal, Australian researcher James Hester provides "a simple formal approach when developing and working with data standards." Using ontology logs or "ologs" — category-theoretic box and arrow diagrams that visually explains mapping elements of sets — and friendly file formats, adapters, and modules, Hester presents several applications towards a useful scientific data transfer network. He concludes: "These ontologies nevertheless capture all scientifically-relevant prior knowledge, and when expressed in machine-readable form are sufficiently expressive to mediate translation between legacy and modern data formats." This results in "a modular, universal data file input and translation system [that] can be implemented without the need for an intermediate format to be defined."
Posted on November 2, 2016
By John Jones
Journal articles

Brandão
et al. at the University of Minho in Portugal needed a practical business intelligence (BI) solution for the Centro Materno Infantil do Norte (CMIN) hospital, particularly to assist with tasks related to gynecology and obstetrics (GO) and voluntary interruption of pregnancy (VIP). In particular, the group needed "to visualize the knowledge extracted from the data stored in information systems in CMIN, through their representation in tables, charts, and tables, among others, but also by integrating DM predictive models." The group set about researching various options, documenting their process along the way. This journal article, published in late 2016, walks through the entire evaluation process, providing a glimpse of how BI applications are relevant to the healthcare industry.
Posted on October 25, 2016
By John Jones
Journal articles

Researchers at ETH Zürich, finding that many commercial laboratory informatics options "affordable to academic labs had either unsuitable user interfaces (UI) or lack of features," decided to look at open-source options. However, like others, they also found some pure open-source options lacked necessary regulatory and high-throughput support. Barilliari
et al. decided to go the "build your own" route, expanding on the existing openBIS platform and adding laboratory information management system (LIMS) and electronic laboratory notebook (ELN) functionality. This brief paper, published in late 2015 in
Bioinformatics, gives a quick overview of the software and how it operates.
Posted on October 18, 2016
By John Jones
Journal articles
In this 2016 paper published in the
Journal of Medical Internet Research, Mackert
et al. review the state of patients' health literacy and how it relates to perceived ease-of-use and the usefulness of the health technology used. The group asked study participants about experiences with fitness apps, nutrition apps, activity trackers, and patient portals, noting afterwards an association between HIT adoption and higher health literacy. They conclude that "HIT has tremendous potential to improve the health of users, and this study is a crucial step toward better understanding how health literacy is associated with HIT adoption and ensuring that users of all levels of health literacy can realize those benefits."
Posted on October 12, 2016
By John Jones
Journal articles
In the various domains of scientific research — including computational biology — the need for better visualization of experimental and research data continues to grow. Whether it's home-grown solutions or open-source solutions, software that can take a wide variety of data and quickly output it in a visualization such as a Venn or Euler diagram is a useful commodity. In this 2016 paper published in
BMC Bioinformatics, researchers at the Ontario Institute for Cancer Research outline their R-friendly, integrable creation VennDiagramWeb, which "allows real-time modification of Venn and Euler diagrams, with parameter setting through a web interface and immediate visualization of results."
Posted on October 3, 2016
By John Jones
Journal articles
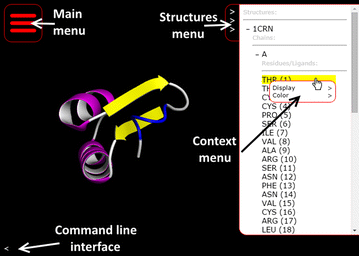
To encourage a move to allow mobile devices to better take advantage of molecular viewing techniques without having to create an application for every OS and environment, why not take advantage of more powerful GPU hardware accelleration in mobile devices? This is the train of thought Bekker
et al. take with their open-source, browser-based molecular viewing software Molmil, used extensively on the Protein Data Bank Japan project. Adding in support for highly detailed polygon models, realistic shaders, easy loading and saving of files, and a command-line interface, the group touts Molil as a strong option for the mobile environment. This 2016 paper further describes the software and its implementation.
Posted on September 26, 2016
By John Jones
Journal articles

No doubt, the traditional paper laboratory notebook isn't quite enough in many of today's modern labs. The research and fabrication labs of the National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) are no exception. This late 2015 paper published in the
Journal of Research of NIST expands upon the changing technological needs for a better and improved laboratory notebook, even beyond the largely software-focused electronic laboratory notebook (ELN). Gates
et al. discuss how they added the hardware component with their push for a “smart” electronic laboratory notebook (SELN) that is portable, intuitive, collaborative, and usable on tablet-based hardware in a cleanroom. They conclude their SELN "provides a comfortable portability and connectivity crucial to its role, and could actually also serve as a desktop replacement for many who do not require extremely powerful computing resources."
Posted on September 20, 2016
By John Jones
Journal articles

In this late 2015 review and background article, Goldberg
et al. provide the details of discussions held during meetings leading up to a February 2016 colloquium hosted by the American Academy of Microbiology on the
Applications of Clinical Microbial Next-Generation Sequencing. The details of these meetings reveal the state of next-generation sequencing, its clinical applications, and the regulatory, financial, and research barriers that exist in NGS' further expansion in clinical settings. They conclude that "[t]he rapid evolution of NGS challenges both the regulatory framework and the development of laboratory standards and will require additional funding and incentives to drive tangible improvements and progress" to realize "the potential benefit that NGS has for patients and their families."
Posted on September 12, 2016
By John Jones
Journal articles

Aronson
et al. of Partners HealthCare and their Laboratory for Molecular Medicine (LMM) experienced first-hand the process of developing infrastructure for the germline genetic testing process. In this 2016 paper published in
Journal of Personalized Medicine, the group shares its experiences of that process, from designating necessary support infrastructure (including a self-developed tool called GeneInsight Clinic) to its integration with other systems such as electronic health records, case management system, and laboratory information systems. They close by stating "a need for an application that interfaces with the range of systems" in the genetic testing environment and that "[s]uch a system could provide the basis for enhanced clinical decision support infrastructure."
Posted on September 6, 2016
By John Jones
Journal articles

"Defining and organizing the set of metadata that is relevant, informative and applicable to diverse experimental techniques is challenging," the team of Hong
et al. state in the introduction of this 2016 paper published in
Database. But the team, motivated by the Encyclopedia of DNA Elements (ENCODE) project and its offshoots, explain and demonstrate their metadata standard and its viability across many types of genomic assays and projects. The group believes that the standard's flexibility and ability to allow for transparent and reproducible experimental data offer much potential. "[A]long with its organizing principles and key features for implementation," they conclude, "[it] could be widely adopted as an open LIMS system."
Posted on August 30, 2016
By John Jones
Journal articles
This 2016 paper by Bianchi
et al., published in
Frontiers in Genetics, takes a closer look at the major issues concerning next-generations sequencing (NGS) technology. The group raises five main concerns than an NGS research group should be aware of before approaching NGS technologies and briefly states positives and negatives to the most current popular tools. The group concludes "[a]lthough larger groups with enough computational members may prefer to develop and maintain their own tailored frameworks, smaller laboratories would save resources and improve their results by adopting solutions developed by third parties," including open-source and cloud-based tools.
Posted on August 24, 2016
By John Jones
Journal articles

Most researchers in the life sciences know now of the concept of "big data" and the push to better organize and mine the data that comes out of biological research. However, the techniques used to mine promising and interesting information from accumulating biological datasets are still developing. In this 2016 paper published in
Bioinformatics and Biology Insights, Naulaerts
et al. look at three specific software tools for mining and presenting useful biological data from complex datasets. They conclude that while the Apriori and arules software tools have their benefits and drawbacks, "MIME showed its value when subsequent mining steps were required" and is inherently easy-to-use.
Posted on August 15, 2016
By John Jones
Journal articles

In this 2016 paper published in
Journal of Pathology Informatics, Cervin
et al. look at the state of pathology reporting, in particular that of structured or synoptic reporting. The group write about their prototype system that "sees reporting as an activity interleaved with image review rather than a separate final step," one that has "an interface to collect, sort, and display findings for the most common reporting needs, such as tumor size, grading, and scoring." They conclude that their synoptic reporting approach to pathology + imaging can provide a level of simplification to improve pathologists' time to report as well ability to communicate with the referring physician.
Posted on August 8, 2016
By John Jones
Journal articles
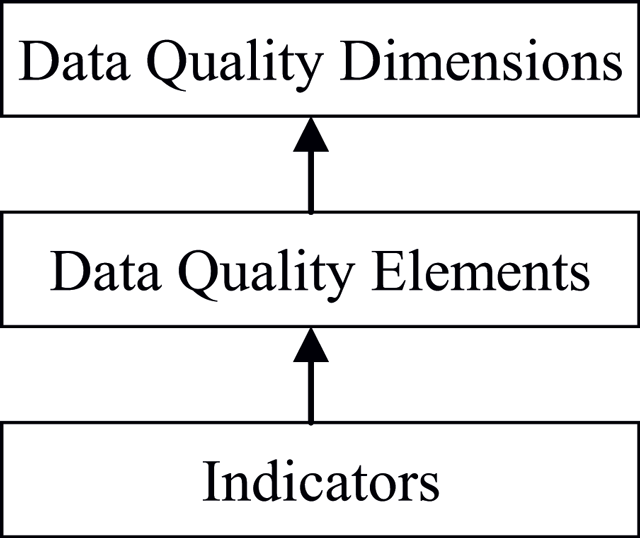
While big data is a popular topic these days, the quality of that data is at times overlooked. This 2015 paper published in
Data Science Journal attempts to address that importance and lay out a framework for big data quality assessment. After conducting a literature review on the topic, Cai and Zhu analyzed the challenges associated with ensuring quality of big data. "Poor data quality will lead to low data utilization efficiency and even bring serious decision-making mistakes," they conclude, presenting "a dynamic big data quality assessment process with a feedback mechanism, which has laid a good foundation for further study of the assessment model."
 In this short paper, Williams et al. of the University of Michigan provide a brief technical view of microservices and how they have the potential to improve the organization and use of bioinformatics and other healthcare applications. They propose that "a well-established software design and deployment strategy" that uses micorservices framework can improve the collaborative and patient-focused efforts of researchers and laboratorians everywhere. They conclude that bioinformaticians, pathologists, and other laboratorians "can contain ever-expanding IT costs, reduce the likelihood of IT implementation mishaps and failures, and perhaps most importantly, greatly elevate the level of service" with properly implemented microservice-based versions of the software they use.
In this short paper, Williams et al. of the University of Michigan provide a brief technical view of microservices and how they have the potential to improve the organization and use of bioinformatics and other healthcare applications. They propose that "a well-established software design and deployment strategy" that uses micorservices framework can improve the collaborative and patient-focused efforts of researchers and laboratorians everywhere. They conclude that bioinformaticians, pathologists, and other laboratorians "can contain ever-expanding IT costs, reduce the likelihood of IT implementation mishaps and failures, and perhaps most importantly, greatly elevate the level of service" with properly implemented microservice-based versions of the software they use.
 In this 2016 article published in JMIR Medical Informatics, Kruse et al. of the Texas State University present the results of a systematic review of articles and studies involving big data in the health care sphere. From this review the team identified nine challenges and 11 opportunities that big data brings to health care. The group describes these challenges and opportunities, concluding that either way "the vast amounts of information generated annually within health care must be organized and compartmentalized to enable universal accessibility and transparency between health care organizations."
In this 2016 article published in JMIR Medical Informatics, Kruse et al. of the Texas State University present the results of a systematic review of articles and studies involving big data in the health care sphere. From this review the team identified nine challenges and 11 opportunities that big data brings to health care. The group describes these challenges and opportunities, concluding that either way "the vast amounts of information generated annually within health care must be organized and compartmentalized to enable universal accessibility and transparency between health care organizations."
 Moving data between systems via an electronic exchange (interoperability) while keeping it clean is always a challenge. Data exchanged between electronic health records (EHR) and immunization information system (IIS) is no exception, as Woinarowicz and Howell demonstrate in this 2016 paper published in Online Journal of Public Health Informatics. Working for the North Dakota Department of Health, Division of Disease Control, the duo explain how setting up their IIS for interoperability with provider EHRs "has had an impact on NDIIS data quality." They conclude: "Timeliness of data entry has improved and overall doses administered have remained fairly consistent, as have the immunization rates ... [but more] will need to be done by NDIIS staff and its vendor to help reduce the negative impact of duplicate record creation, as well as data completeness."
Moving data between systems via an electronic exchange (interoperability) while keeping it clean is always a challenge. Data exchanged between electronic health records (EHR) and immunization information system (IIS) is no exception, as Woinarowicz and Howell demonstrate in this 2016 paper published in Online Journal of Public Health Informatics. Working for the North Dakota Department of Health, Division of Disease Control, the duo explain how setting up their IIS for interoperability with provider EHRs "has had an impact on NDIIS data quality." They conclude: "Timeliness of data entry has improved and overall doses administered have remained fairly consistent, as have the immunization rates ... [but more] will need to be done by NDIIS staff and its vendor to help reduce the negative impact of duplicate record creation, as well as data completeness."
 Genomic data is increasingly used to provide better, more focused clinical care. Or course, its associated datasets can be large, and it can take significant processing power to utilize and manage effectively. In this 2016 paper published in Journal of Personalized Medicine, Tsai et al. of Partners Healthcare describe their "bioinformatics strategy to efficiently process and deliver genomic data to geneticists for clinical interpretation." They conclude that with more research comes improved workflows and "filtrations that include larger portions of the non-coding regions as they start to have utility in the clinical setting, ultimately enabling the full utility of complete genome sequencing."
Genomic data is increasingly used to provide better, more focused clinical care. Or course, its associated datasets can be large, and it can take significant processing power to utilize and manage effectively. In this 2016 paper published in Journal of Personalized Medicine, Tsai et al. of Partners Healthcare describe their "bioinformatics strategy to efficiently process and deliver genomic data to geneticists for clinical interpretation." They conclude that with more research comes improved workflows and "filtrations that include larger portions of the non-coding regions as they start to have utility in the clinical setting, ultimately enabling the full utility of complete genome sequencing."
 Synoptic reporting is an important part of not only managing patient testing information but also reporting that data for research and data mining purposes. As such, the extraction of particular elements from these types of reports — including those recording major cancer information — has historically been difficult. Recent developments in extracting key information from synoptic reports have made it easier, however, including the use of the R programming language. In this paper by J.J. Ye, the process of extracting melanoma data from pathology datasets is used to describe a broader, wide-ranging application of R and the associated RODBC package for extracting useful data from synoptic reports. Ye concludes: "This approach can be easily modified and adopted for other pathology information systems that use relational database for data management."
Synoptic reporting is an important part of not only managing patient testing information but also reporting that data for research and data mining purposes. As such, the extraction of particular elements from these types of reports — including those recording major cancer information — has historically been difficult. Recent developments in extracting key information from synoptic reports have made it easier, however, including the use of the R programming language. In this paper by J.J. Ye, the process of extracting melanoma data from pathology datasets is used to describe a broader, wide-ranging application of R and the associated RODBC package for extracting useful data from synoptic reports. Ye concludes: "This approach can be easily modified and adopted for other pathology information systems that use relational database for data management."
 In this 2016 paper published in Data Science Journal, Australian researcher James Hester provides "a simple formal approach when developing and working with data standards." Using ontology logs or "ologs" — category-theoretic box and arrow diagrams that visually explains mapping elements of sets — and friendly file formats, adapters, and modules, Hester presents several applications towards a useful scientific data transfer network. He concludes: "These ontologies nevertheless capture all scientifically-relevant prior knowledge, and when expressed in machine-readable form are sufficiently expressive to mediate translation between legacy and modern data formats." This results in "a modular, universal data file input and translation system [that] can be implemented without the need for an intermediate format to be defined."
In this 2016 paper published in Data Science Journal, Australian researcher James Hester provides "a simple formal approach when developing and working with data standards." Using ontology logs or "ologs" — category-theoretic box and arrow diagrams that visually explains mapping elements of sets — and friendly file formats, adapters, and modules, Hester presents several applications towards a useful scientific data transfer network. He concludes: "These ontologies nevertheless capture all scientifically-relevant prior knowledge, and when expressed in machine-readable form are sufficiently expressive to mediate translation between legacy and modern data formats." This results in "a modular, universal data file input and translation system [that] can be implemented without the need for an intermediate format to be defined."
 Brandão et al. at the University of Minho in Portugal needed a practical business intelligence (BI) solution for the Centro Materno Infantil do Norte (CMIN) hospital, particularly to assist with tasks related to gynecology and obstetrics (GO) and voluntary interruption of pregnancy (VIP). In particular, the group needed "to visualize the knowledge extracted from the data stored in information systems in CMIN, through their representation in tables, charts, and tables, among others, but also by integrating DM predictive models." The group set about researching various options, documenting their process along the way. This journal article, published in late 2016, walks through the entire evaluation process, providing a glimpse of how BI applications are relevant to the healthcare industry.
Brandão et al. at the University of Minho in Portugal needed a practical business intelligence (BI) solution for the Centro Materno Infantil do Norte (CMIN) hospital, particularly to assist with tasks related to gynecology and obstetrics (GO) and voluntary interruption of pregnancy (VIP). In particular, the group needed "to visualize the knowledge extracted from the data stored in information systems in CMIN, through their representation in tables, charts, and tables, among others, but also by integrating DM predictive models." The group set about researching various options, documenting their process along the way. This journal article, published in late 2016, walks through the entire evaluation process, providing a glimpse of how BI applications are relevant to the healthcare industry.
 Researchers at ETH Zürich, finding that many commercial laboratory informatics options "affordable to academic labs had either unsuitable user interfaces (UI) or lack of features," decided to look at open-source options. However, like others, they also found some pure open-source options lacked necessary regulatory and high-throughput support. Barilliari et al. decided to go the "build your own" route, expanding on the existing openBIS platform and adding laboratory information management system (LIMS) and electronic laboratory notebook (ELN) functionality. This brief paper, published in late 2015 in Bioinformatics, gives a quick overview of the software and how it operates.
Researchers at ETH Zürich, finding that many commercial laboratory informatics options "affordable to academic labs had either unsuitable user interfaces (UI) or lack of features," decided to look at open-source options. However, like others, they also found some pure open-source options lacked necessary regulatory and high-throughput support. Barilliari et al. decided to go the "build your own" route, expanding on the existing openBIS platform and adding laboratory information management system (LIMS) and electronic laboratory notebook (ELN) functionality. This brief paper, published in late 2015 in Bioinformatics, gives a quick overview of the software and how it operates.
 In this 2016 paper published in the Journal of Medical Internet Research, Mackert et al. review the state of patients' health literacy and how it relates to perceived ease-of-use and the usefulness of the health technology used. The group asked study participants about experiences with fitness apps, nutrition apps, activity trackers, and patient portals, noting afterwards an association between HIT adoption and higher health literacy. They conclude that "HIT has tremendous potential to improve the health of users, and this study is a crucial step toward better understanding how health literacy is associated with HIT adoption and ensuring that users of all levels of health literacy can realize those benefits."
In this 2016 paper published in the Journal of Medical Internet Research, Mackert et al. review the state of patients' health literacy and how it relates to perceived ease-of-use and the usefulness of the health technology used. The group asked study participants about experiences with fitness apps, nutrition apps, activity trackers, and patient portals, noting afterwards an association between HIT adoption and higher health literacy. They conclude that "HIT has tremendous potential to improve the health of users, and this study is a crucial step toward better understanding how health literacy is associated with HIT adoption and ensuring that users of all levels of health literacy can realize those benefits."
 In the various domains of scientific research — including computational biology — the need for better visualization of experimental and research data continues to grow. Whether it's home-grown solutions or open-source solutions, software that can take a wide variety of data and quickly output it in a visualization such as a Venn or Euler diagram is a useful commodity. In this 2016 paper published in BMC Bioinformatics, researchers at the Ontario Institute for Cancer Research outline their R-friendly, integrable creation VennDiagramWeb, which "allows real-time modification of Venn and Euler diagrams, with parameter setting through a web interface and immediate visualization of results."
In the various domains of scientific research — including computational biology — the need for better visualization of experimental and research data continues to grow. Whether it's home-grown solutions or open-source solutions, software that can take a wide variety of data and quickly output it in a visualization such as a Venn or Euler diagram is a useful commodity. In this 2016 paper published in BMC Bioinformatics, researchers at the Ontario Institute for Cancer Research outline their R-friendly, integrable creation VennDiagramWeb, which "allows real-time modification of Venn and Euler diagrams, with parameter setting through a web interface and immediate visualization of results."
 To encourage a move to allow mobile devices to better take advantage of molecular viewing techniques without having to create an application for every OS and environment, why not take advantage of more powerful GPU hardware accelleration in mobile devices? This is the train of thought Bekker et al. take with their open-source, browser-based molecular viewing software Molmil, used extensively on the Protein Data Bank Japan project. Adding in support for highly detailed polygon models, realistic shaders, easy loading and saving of files, and a command-line interface, the group touts Molil as a strong option for the mobile environment. This 2016 paper further describes the software and its implementation.
To encourage a move to allow mobile devices to better take advantage of molecular viewing techniques without having to create an application for every OS and environment, why not take advantage of more powerful GPU hardware accelleration in mobile devices? This is the train of thought Bekker et al. take with their open-source, browser-based molecular viewing software Molmil, used extensively on the Protein Data Bank Japan project. Adding in support for highly detailed polygon models, realistic shaders, easy loading and saving of files, and a command-line interface, the group touts Molil as a strong option for the mobile environment. This 2016 paper further describes the software and its implementation.
 No doubt, the traditional paper laboratory notebook isn't quite enough in many of today's modern labs. The research and fabrication labs of the National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) are no exception. This late 2015 paper published in the Journal of Research of NIST expands upon the changing technological needs for a better and improved laboratory notebook, even beyond the largely software-focused electronic laboratory notebook (ELN). Gates et al. discuss how they added the hardware component with their push for a “smart” electronic laboratory notebook (SELN) that is portable, intuitive, collaborative, and usable on tablet-based hardware in a cleanroom. They conclude their SELN "provides a comfortable portability and connectivity crucial to its role, and could actually also serve as a desktop replacement for many who do not require extremely powerful computing resources."
No doubt, the traditional paper laboratory notebook isn't quite enough in many of today's modern labs. The research and fabrication labs of the National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) are no exception. This late 2015 paper published in the Journal of Research of NIST expands upon the changing technological needs for a better and improved laboratory notebook, even beyond the largely software-focused electronic laboratory notebook (ELN). Gates et al. discuss how they added the hardware component with their push for a “smart” electronic laboratory notebook (SELN) that is portable, intuitive, collaborative, and usable on tablet-based hardware in a cleanroom. They conclude their SELN "provides a comfortable portability and connectivity crucial to its role, and could actually also serve as a desktop replacement for many who do not require extremely powerful computing resources."
 In this late 2015 review and background article, Goldberg et al. provide the details of discussions held during meetings leading up to a February 2016 colloquium hosted by the American Academy of Microbiology on the Applications of Clinical Microbial Next-Generation Sequencing. The details of these meetings reveal the state of next-generation sequencing, its clinical applications, and the regulatory, financial, and research barriers that exist in NGS' further expansion in clinical settings. They conclude that "[t]he rapid evolution of NGS challenges both the regulatory framework and the development of laboratory standards and will require additional funding and incentives to drive tangible improvements and progress" to realize "the potential benefit that NGS has for patients and their families."
In this late 2015 review and background article, Goldberg et al. provide the details of discussions held during meetings leading up to a February 2016 colloquium hosted by the American Academy of Microbiology on the Applications of Clinical Microbial Next-Generation Sequencing. The details of these meetings reveal the state of next-generation sequencing, its clinical applications, and the regulatory, financial, and research barriers that exist in NGS' further expansion in clinical settings. They conclude that "[t]he rapid evolution of NGS challenges both the regulatory framework and the development of laboratory standards and will require additional funding and incentives to drive tangible improvements and progress" to realize "the potential benefit that NGS has for patients and their families."
 Aronson et al. of Partners HealthCare and their Laboratory for Molecular Medicine (LMM) experienced first-hand the process of developing infrastructure for the germline genetic testing process. In this 2016 paper published in Journal of Personalized Medicine, the group shares its experiences of that process, from designating necessary support infrastructure (including a self-developed tool called GeneInsight Clinic) to its integration with other systems such as electronic health records, case management system, and laboratory information systems. They close by stating "a need for an application that interfaces with the range of systems" in the genetic testing environment and that "[s]uch a system could provide the basis for enhanced clinical decision support infrastructure."
Aronson et al. of Partners HealthCare and their Laboratory for Molecular Medicine (LMM) experienced first-hand the process of developing infrastructure for the germline genetic testing process. In this 2016 paper published in Journal of Personalized Medicine, the group shares its experiences of that process, from designating necessary support infrastructure (including a self-developed tool called GeneInsight Clinic) to its integration with other systems such as electronic health records, case management system, and laboratory information systems. They close by stating "a need for an application that interfaces with the range of systems" in the genetic testing environment and that "[s]uch a system could provide the basis for enhanced clinical decision support infrastructure."
 "Defining and organizing the set of metadata that is relevant, informative and applicable to diverse experimental techniques is challenging," the team of Hong et al. state in the introduction of this 2016 paper published in Database. But the team, motivated by the Encyclopedia of DNA Elements (ENCODE) project and its offshoots, explain and demonstrate their metadata standard and its viability across many types of genomic assays and projects. The group believes that the standard's flexibility and ability to allow for transparent and reproducible experimental data offer much potential. "[A]long with its organizing principles and key features for implementation," they conclude, "[it] could be widely adopted as an open LIMS system."
"Defining and organizing the set of metadata that is relevant, informative and applicable to diverse experimental techniques is challenging," the team of Hong et al. state in the introduction of this 2016 paper published in Database. But the team, motivated by the Encyclopedia of DNA Elements (ENCODE) project and its offshoots, explain and demonstrate their metadata standard and its viability across many types of genomic assays and projects. The group believes that the standard's flexibility and ability to allow for transparent and reproducible experimental data offer much potential. "[A]long with its organizing principles and key features for implementation," they conclude, "[it] could be widely adopted as an open LIMS system."
 This 2016 paper by Bianchi et al., published in Frontiers in Genetics, takes a closer look at the major issues concerning next-generations sequencing (NGS) technology. The group raises five main concerns than an NGS research group should be aware of before approaching NGS technologies and briefly states positives and negatives to the most current popular tools. The group concludes "[a]lthough larger groups with enough computational members may prefer to develop and maintain their own tailored frameworks, smaller laboratories would save resources and improve their results by adopting solutions developed by third parties," including open-source and cloud-based tools.
This 2016 paper by Bianchi et al., published in Frontiers in Genetics, takes a closer look at the major issues concerning next-generations sequencing (NGS) technology. The group raises five main concerns than an NGS research group should be aware of before approaching NGS technologies and briefly states positives and negatives to the most current popular tools. The group concludes "[a]lthough larger groups with enough computational members may prefer to develop and maintain their own tailored frameworks, smaller laboratories would save resources and improve their results by adopting solutions developed by third parties," including open-source and cloud-based tools.
 Most researchers in the life sciences know now of the concept of "big data" and the push to better organize and mine the data that comes out of biological research. However, the techniques used to mine promising and interesting information from accumulating biological datasets are still developing. In this 2016 paper published in Bioinformatics and Biology Insights, Naulaerts et al. look at three specific software tools for mining and presenting useful biological data from complex datasets. They conclude that while the Apriori and arules software tools have their benefits and drawbacks, "MIME showed its value when subsequent mining steps were required" and is inherently easy-to-use.
Most researchers in the life sciences know now of the concept of "big data" and the push to better organize and mine the data that comes out of biological research. However, the techniques used to mine promising and interesting information from accumulating biological datasets are still developing. In this 2016 paper published in Bioinformatics and Biology Insights, Naulaerts et al. look at three specific software tools for mining and presenting useful biological data from complex datasets. They conclude that while the Apriori and arules software tools have their benefits and drawbacks, "MIME showed its value when subsequent mining steps were required" and is inherently easy-to-use.
 In this 2016 paper published in Journal of Pathology Informatics, Cervin et al. look at the state of pathology reporting, in particular that of structured or synoptic reporting. The group write about their prototype system that "sees reporting as an activity interleaved with image review rather than a separate final step," one that has "an interface to collect, sort, and display findings for the most common reporting needs, such as tumor size, grading, and scoring." They conclude that their synoptic reporting approach to pathology + imaging can provide a level of simplification to improve pathologists' time to report as well ability to communicate with the referring physician.
In this 2016 paper published in Journal of Pathology Informatics, Cervin et al. look at the state of pathology reporting, in particular that of structured or synoptic reporting. The group write about their prototype system that "sees reporting as an activity interleaved with image review rather than a separate final step," one that has "an interface to collect, sort, and display findings for the most common reporting needs, such as tumor size, grading, and scoring." They conclude that their synoptic reporting approach to pathology + imaging can provide a level of simplification to improve pathologists' time to report as well ability to communicate with the referring physician.
 While big data is a popular topic these days, the quality of that data is at times overlooked. This 2015 paper published in Data Science Journal attempts to address that importance and lay out a framework for big data quality assessment. After conducting a literature review on the topic, Cai and Zhu analyzed the challenges associated with ensuring quality of big data. "Poor data quality will lead to low data utilization efficiency and even bring serious decision-making mistakes," they conclude, presenting "a dynamic big data quality assessment process with a feedback mechanism, which has laid a good foundation for further study of the assessment model."
While big data is a popular topic these days, the quality of that data is at times overlooked. This 2015 paper published in Data Science Journal attempts to address that importance and lay out a framework for big data quality assessment. After conducting a literature review on the topic, Cai and Zhu analyzed the challenges associated with ensuring quality of big data. "Poor data quality will lead to low data utilization efficiency and even bring serious decision-making mistakes," they conclude, presenting "a dynamic big data quality assessment process with a feedback mechanism, which has laid a good foundation for further study of the assessment model."
















