Posted on February 27, 2023
By LabLynx
Journal articles
In this 2022 paper published in the
Egyptian Journal of Forensic Sciences, Prahladh and van Wyk provide a first-of-its-kind comprehensive scoping review of "articles involving unnatural deaths, focused on data practice or data management systems, relating to forensic medicine, all study designs, and published in English," with the goal of being able to draw conclusions about the current academic view of forensic data management. After examining more than 23,000 articles, the authors were only able to find 16 that met their criteria, according to their stated methodology. After a thorough review of those 16 articles, the duo concludes that "the literature shows that electronic data reporting systems are relevant and were developed from the recognition of coronial data as not only a part of the death investigation but as a contributor to preventable death research and public health initiatives." However, there are few lower- and middle-income countries (LMICs) represented in the study, and the authors believe that given how "forensic medicine departments can utilize simple and available tools that can advance standardization of data collection, storage, and reporting," it would behoove more LMICs to consider pilot systems such as "the Nigerian pilot program [that] still managed to contribute to statistically relevant data for impactful research" while using low-cost and readily available data management tools.
Posted on February 21, 2023
By LabLynx
Journal articles
From disparate pools of data and information to inefficiencies in using that disparate data and information, the academic cancer center wishing to operate more effectively while improving patient outcomes and enabling more impactful research must turn to well-implemented data management systems and integrations. The University of Rochester Medical Center's James P. Wilmot Cancer Institute (WCI) was no exception to this greater need, turning to developing a custom data management platform called Hyperion to meet their needs. In this 2022 paper published in
PLOS Digital Health, key stakeholders of Hyperion at WCI present the background on cancer center data management, as well as their methods in developing and results in using Hyperion. They follow this with discussion of their results, concluding that "Hyperion has surmounted large challenges in working with healthcare data to merge, organize, validate, and package data for use in multiple applications" at WCI, while also "lowering the skill floor for interaction with and maintenance of the software, reducing costs, and encouraging user autonomy." They add that a similar such system, from their viewpoint, could provide similar benefits in other academic cancer centers.
Posted on February 13, 2023
By LabLynx
Journal articles
In this 2022 journal article published in
Metabolites, Djilali
et al. present the results of a literature review "of studies performed on the effects of different storage conditions on the stability of cannabis compounds present in various biological matrices." Noting a growing need for accurate testing for the presence of cannabis compounds in humans, the authors first review the state of analysis among conventional biological matrices (i.e., blood, plasma, urine, and oral fluids) before looking at alternative matrices (i.e., breath, bile fluid, hair, sweat, cerumen, and dried blood spots). From their literature analysis, the authors made several conclusions about the various matrices, their collection methods, and their testing. Depending on the matrix, the authors recommended specific sample containers and storage temperatures among the conventional matrices, while noting that more research is required concerning laboratory testing of alternative matrices.
Posted on February 7, 2023
By LabLynx
Journal articles
In this 2022 article published in the journal
BMC Medical Ethics, Scheibner
et al. present an assessment of Swiss hospital and medical research experts' views on using advanced technical solutions towards "sharing patient data in a privacy-preserving manner." In particular, the authors examine homomorphic encryption (HE) and distributed ledger technology (DLT) in the scope of European and Swiss regulatory frameworks. After an in-depth introduction on the topic, the authors present their methodology (an interview study) and their results, which touch upon five different information request scenarios. They then discuss the legal, ethical, and compatibility issues associated with using HE and DLT towards the problem of privacy-preserving patient data. They conclude that "a holistic approach needs to be taken to introducing HE and DLT as a mechanism for patient data management," one that tends "to recognize that social license and public trust from patients and physicians is as important as legal compliance."
Posted on January 31, 2023
By LabLynx
Journal articles
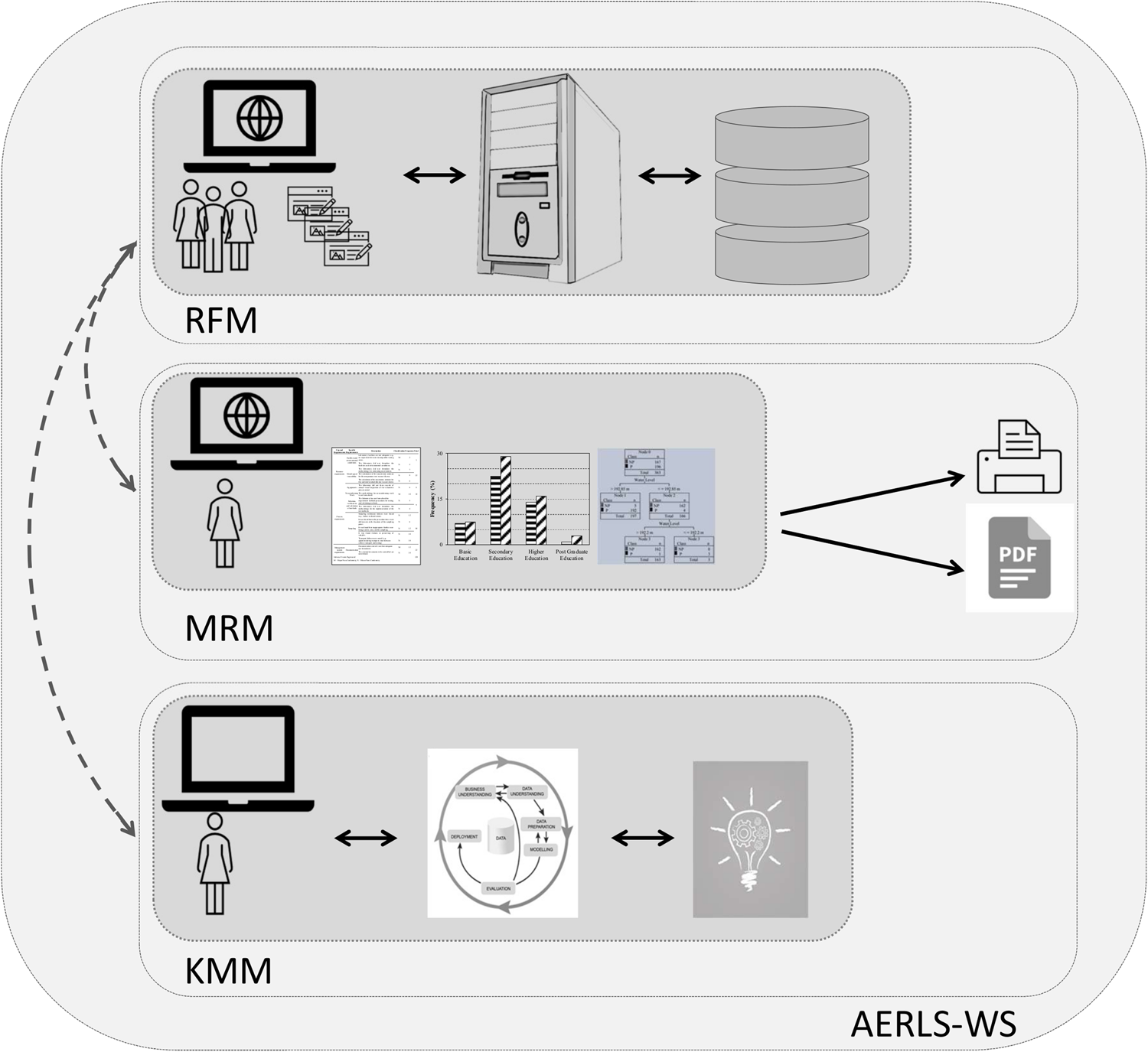
This 2022 journal article published in
AQUA - Water infrastructure, Ecosystems and Society sees Fernandes
et al. presenting a computerized "system for reporting and learning from adverse events" in water sampling and analysis laboratories. The work was prompted by "a high frequency of adverse events in connection with sampling" at the Water Laboratory of Santiago do Cacém Municipality in Portugal. After introducing the topic of water quality testing and work related to using artificial intelligence (AI) in that testing, the authors describe their method of using a Eindhoven Classification Model (ECM) within the scope of ISO/IEC 17025 requirements. They then discuss the results of their software-based approach and conclude that their modular adverse event reporting and learning system has many strengths, particularly in that it "allows knowledge extraction, i.e., the identification of the main failure causes, possible trends, areas requiring improvement plans, or changes in procedures."
Posted on January 23, 2023
By LabLynx
Journal articles
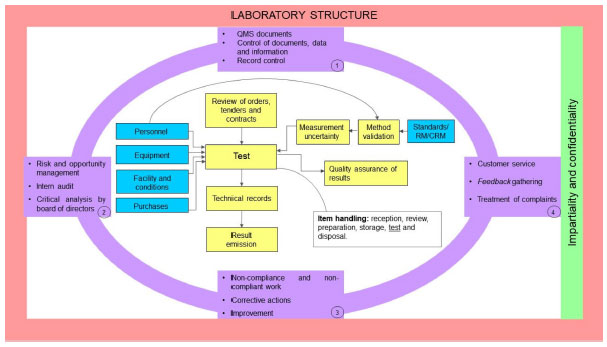
In this 2021 paper publisher in the journal
Química Nova, Miguel
et al. present the ISO/IEC 17025 standard in a historical context, while also providing some additional details about the concepts the standard proposes. As a quality management standard that also addresses competence, impartiality, and consistent operations in the laboratory, the standard emphasizes the importance of well-planned quality assurance towards reliable and traceable laboratory results. After an introduction to the standard, the authors take an in-depth look at ISO/IEC 17025's history and what drove changes to the standard over time. The article then examines what the standard asks of laboratories, as well as what value it adds to those labs. "By enacting ISO/IEC 17025," the authors conclude, "testing and calibration laboratories demonstrate they are responsible with their activities and their impacts, and put quality management and metrological traceability at the forefront of their operations."
Posted on January 16, 2023
By LabLynx
Journal articles
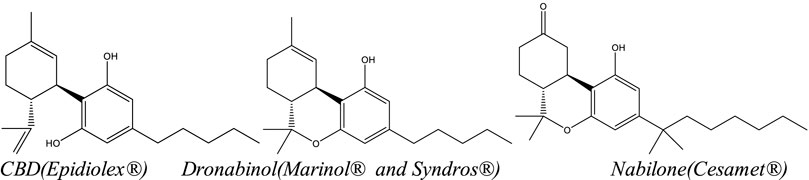
Hemp? Cannabis? Marijuana? Industrial hemp? Salehi
et al. note that terms like these and others are "a significant source of confusion for many," not just in the public but also within industry, marketing, and other groups. This not only causes issues with communicating research clearly but also employing that research to best effect. As such, the authors of this paper, published in the journal
Frontiers in Pharmacology, pose the important question, "What is essential for defining
Cannabis as a food, supplement, or drug?" Salehi
et al. answer this question by reviewing a wide swath of current study on the
Cannabis plant and its derivatives, highlighting critical definitions, composition, production practices, and pharmacological effects as part of defining the essentials of
Cannabis. The authors also go into its use in foods, drugs, and supplements, as well as regulatory status and testing methodologies. They conclude that "despite all of the recent advances, several cannabis topics remain to be addressed," and addressing those topics will require more consistent terminology, greater understanding of the human endocannabinoid system, and a more consistent "platform for developing research about cannabis and related industries" within a number of countries.
Posted on January 9, 2023
By LabLynx
Journal articles
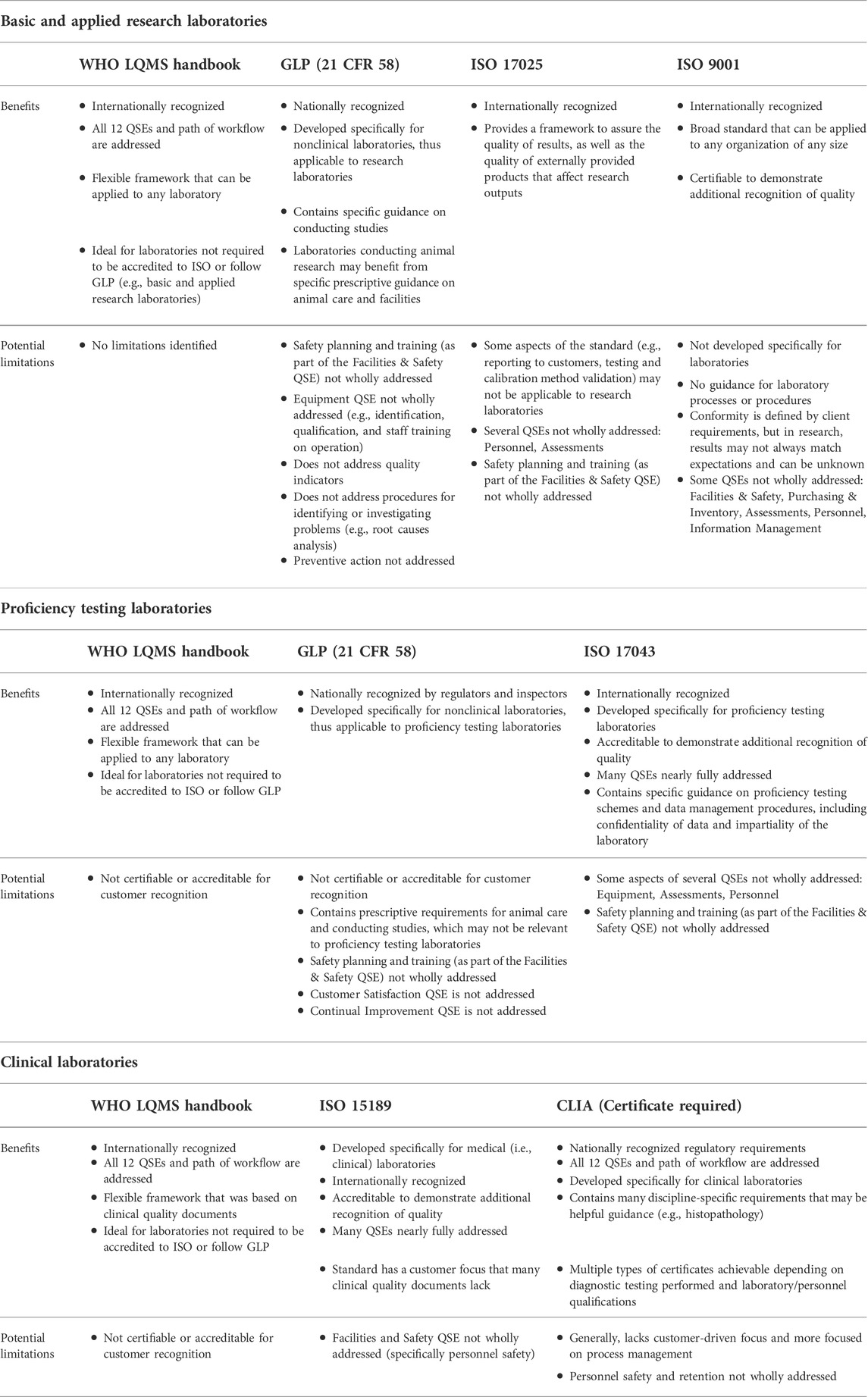
The quality management system (QMS) is increasingly a constant in laboratories of all types, lending support for better products and services coming out those labs. However, as technologies change and new challenges arise in research, medical, analytical, and R&D labs, the need for a more robust QMS becomes more obvious. In this 2022 article published in the journal
Frontiers in Bioengineering and Biotechnology, Pillai
et al. explore the varying frameworks of the QMS, which frameworks are best in which labs, and what implementation considerations should be made. After an informative introduction, the authors define the various laboratory types and match those types to the various QMS frameworks. They then provide a set of three critical recommendations for their implementation and use, concluding that while many frameworks are robust, the modern laboratory may need to incorporate more than one framework in order to fully achieve their quality goals. They add that "a holistic QMS framework complemented with guidance from multiple quality documents can benefit many laboratories that aim to address" the 12 quality system essentials (QSEs) of the Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute (CLSI).
Posted on January 3, 2023
By LabLynx
Journal articles
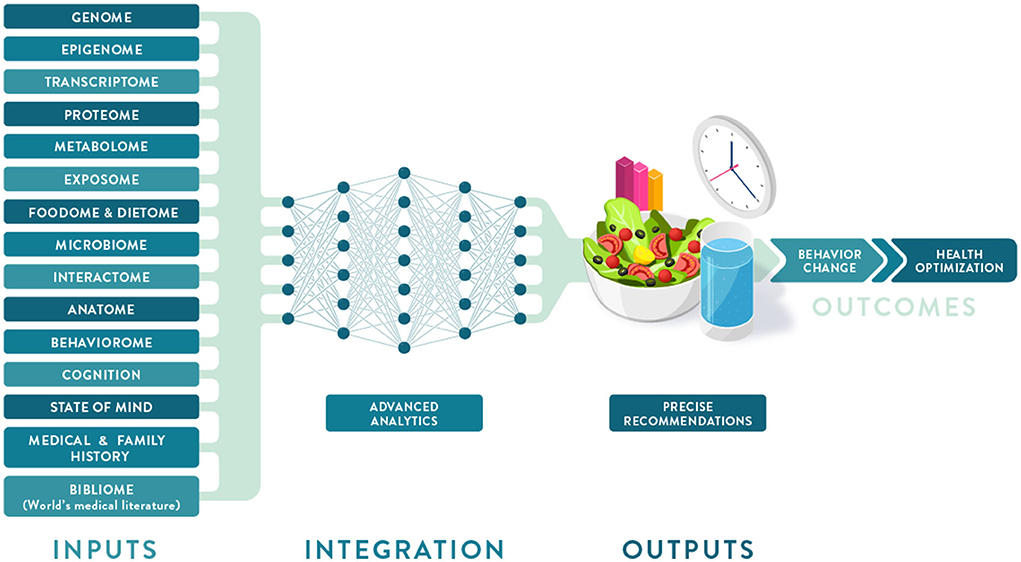
In this 2022 article published in the journal
Frontiers in Nutrition, Berciano
et al. discuss the topic of precision or personalized nutrition (PN) in the context of needing advancements in analytical and data management technologies in order to reach its full potential. After a brief introduction and discussion of the concept of PN, the authors examine the role of big data and data analysis in PN, particularly in regards to developing and optimizing personalized nutrition products and services. They then couch PN in terms of it having the potential to be "the future of healthcare," addressing topics such as phenotyping, metabolic methods, environmental factors, and the role of money and medical service insurers. After compiling a set of best practices and standards in PN and addressing the need for advocacy efforts towards PN, the authors conclude that while "PN should have an impact on both personal and public health ... [a]dvancing the science and the adoption of PN will require a significant investment in multidisciplinary collaborations that translate the fast-moving technological advances in omics, sensors, AI, and big data management and analytics into powerful and user-friendly tools."
Posted on December 19, 2022
By LabLynx
Journal articles
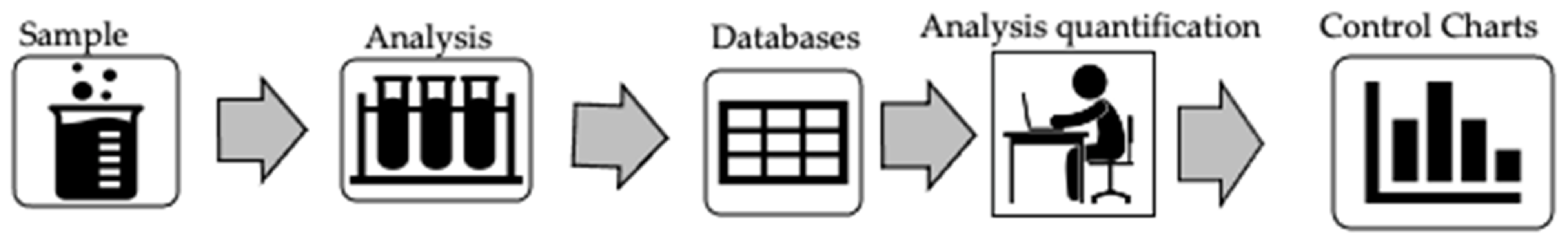
In this 2022 article published in the journal
Sustainability, da Silva
et al. of the Polytechnic Institute of Beja demonstrate the usefulness of control charting in the realm of maintaining water quality. Using a test case of wastewater from a treatment plant associated with a slaughterhouse, the authors describe their materials and methods, which progressed from wastewater sample to analysis and databasing of the results, followed by analysis quantification and control charting. In this article, they show 10 control charts associated with five test variables, demonstrating the usefulness of the control charts in identifying at least one significant set of out-of-specification results, likely associated with a treatment failure at the facility. They conclude that the results demonstrate "how rapid detection of variations in small scales on control charts allows the lab to better act upon identifying potential causes of variability," and they "show it is possible to state that all points are under statistical control, and thus by extension these types of control charts can have routine value in the laboratory."
Posted on December 13, 2022
By LabLynx
Journal articles

In this 2022 paper published in
Talanta Open, Hall
et al. propose an analytical method for 10 cannabis-related cannabinoids that is cost-efficient, rapid, and robust in its use. Noting "elevated cost and limited availability of certified analytical reference standards for some cannabinoids," the authors sought to develop a high-performance liquid chromatography-photodiode array (HPLC-PDA) method for 10 cannabinoids that uses "relative retention times (RRT) for peak identification and relative response factors (RRF) for their quantification." After describing their materials and methods, the authors present their results and discuss their implications towards various aspects such as accuracy, recovery, and quantification. They conclude that their method is robust, acceptably accurate, and has sufficient dynamic range. They add that with their method, "cost barriers for the analysis of panels of cannabinoids can be overcome, such that a diversity of cannabinoids can be analyzed as a part of routine quality control, with results that reflect the therapeutic efficacy for the consumer."
Posted on December 6, 2022
By LabLynx
Journal articles
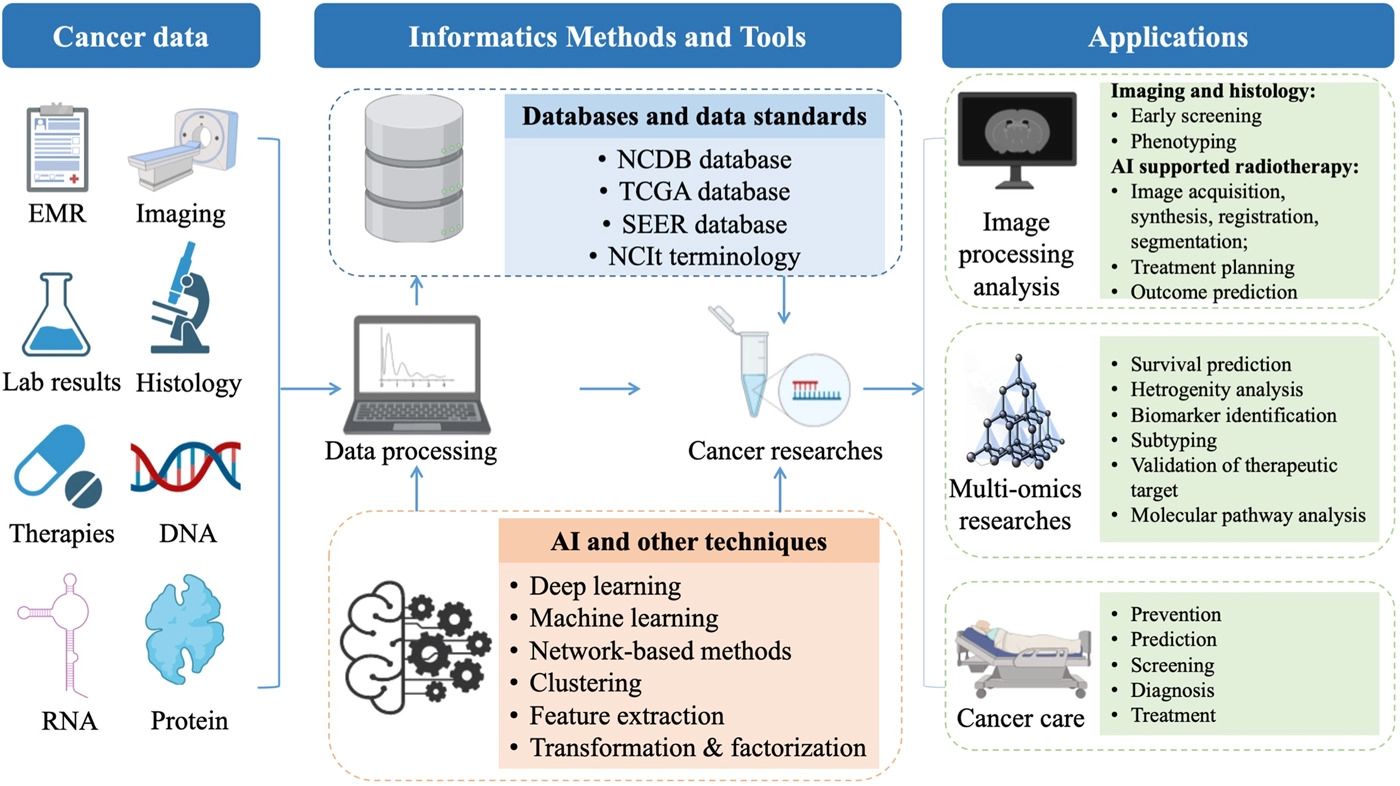
In the age of "big data," appropriately implemented informatics solutions have become more important than ever. This has become particularly important to the world of cancer research and the weighty analyses of "the genome, epigenome, transcriptome, proteome, metabolome, and microbiome" of individuals. In this 2022 journal article by Hong
et al., a review of the current state of cancer informatics is presented, addressing not only current informatics-supported applications but also challenges, opportunities, and future likelihoods. The authors conclude that not only "clinical oncology and research are reaping the benefits of informatics," but also that "with the further development of convenient and intelligent tools, informatics will enable earlier cancer detection, more precise cancer treatment, and better outcomes."
Posted on November 28, 2022
By LabLynx
Journal articles

Interoperable health information systems in the United States has been a long-road effort that, according to Szarfman
et al., has a long way to go yet to reach its full potential. Noting the strain on the digital health systems of hospitals, physician offices, laboratories, and other entities during the COVID-19 pandemic, the authors—many of them from the U.S. FDA—"recommend the implementation of standardized data collection and transmission systems, universal identifiers for individual patients and end users, a reference standard infrastructure to support calibration and integration of laboratory results from equivalent tests, and modernized working practices" in this brief paper. After providing a contextual introduction, they discuss the lack of universal and harmonized data collection and transmission standards and highlight five major issues with modern health systems that need immediate action. After briefly discussing return on investment in adopting the authors' recommendations, they conclude by posting 11 recommendations for U.S. legislators and nine recommendations for public-private partnerships in addressing the issues of health systems interoperability in the United States. They close by noting that while "this problem will not be cheap to fix ... it will be much costlier to ignore."
Posted on November 22, 2022
By LabLynx
Journal articles
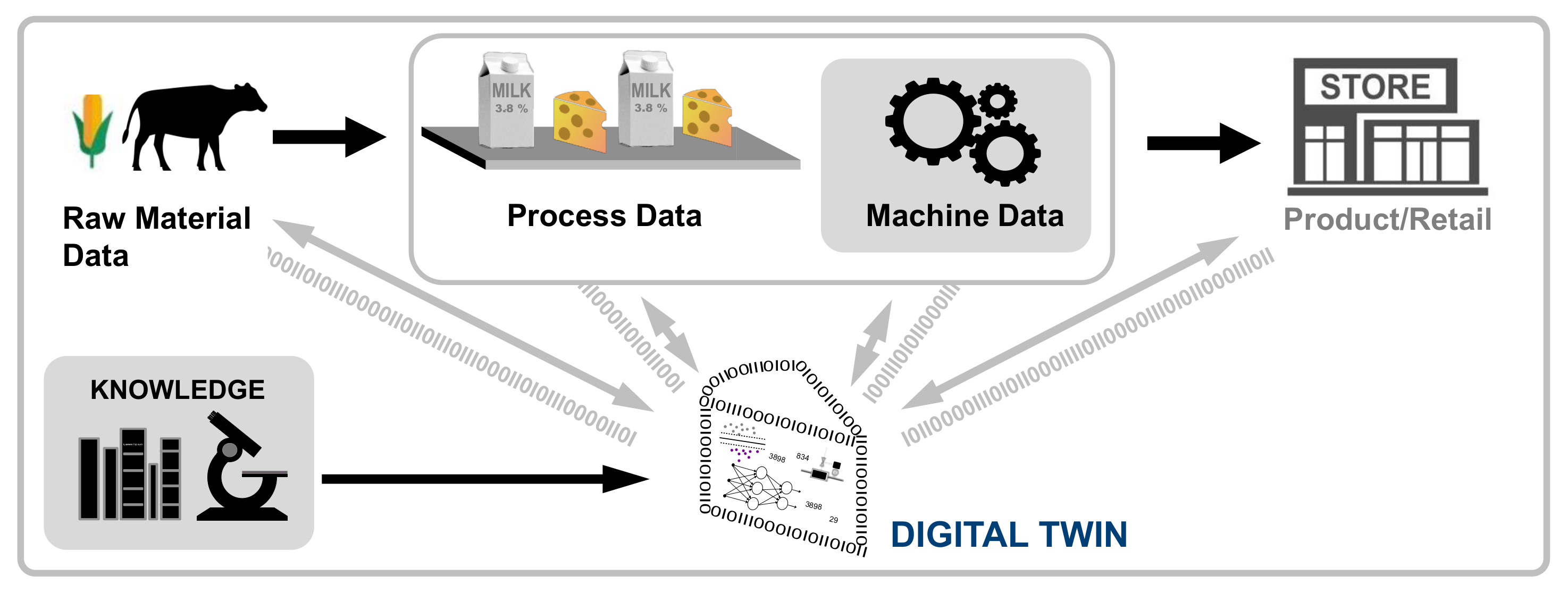
In this 2022 paper published in
Sensors, Henrichs
et al. of the University of Hohenheim present their literature review on the topic of digital twins in the food and beverage industry. The concept of the digital twin—a digital representation of a product, process, or system that as closely as possible represents the characteristics of the physical representation—is relatively new, and its use in the food and beverage industry holds much promise, according to the authors' research. After an introduction and extensive background, the authors provide the methodology for their review, focusing on six critical questions. They then present their results from a broad perspective, and then a more in-depth discussion focusing on answering those six questions. They close by emphasizing related work in the field, and then concluding that while a majority of the research conducted by others involves the production and processing stages of food and beverage activities, a dearth of cases appear to discuss supply, processing, retail, and consumption. They also note that "relatively few focus on the integration of digital twins in systems for developing autonomous control or providing recommendations to humans," which could be practically useful in the industry. "Nevertheless, digital twins provide huge potentials," they add, "e.g., in determining food quality, ensuring traceability, or designing personalized foods."
Posted on November 14, 2022
By LabLynx
Journal articles
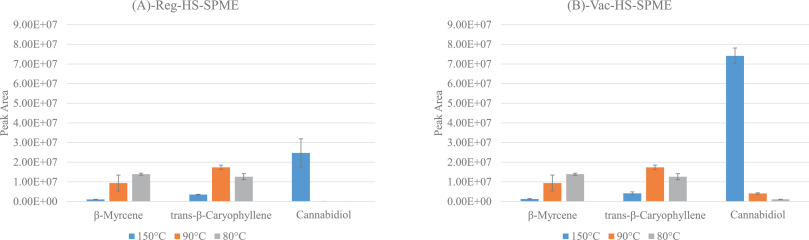
In this 2022 journal article published in
Advances in Sample Preparation, Capetti
et al. of Università di Torino investigate the advantages and disadvantages that vacuum-assisted headspace solid-phase microextraction (Vac-HSSPME) may lend to the process of
Cannabis inflorescence preparation and subsequent testing, by gas chromatography–mass spectrometry (GC-MS), in order to accurately characterize both terpenoid and cannabinoid profiles. After providing an introduction on the topic, the authors describe the materials and methods used, as well as the results of their study. They conclude that "compared to standard HSSPME, vacuum conditions in the headspace ensure the fast recovery of cannabinoid markers at considerably lower sampling temperature (i.e., 90°C) that do not discriminate the most volatile fraction nor cause the formation of artifacts when the sampling time is minimized." They add that, in combination with GC-MS, Vac-HSSPME can prove to be "fast, totally automatable, and solvent-free," representing a more green analytical approach to
Cannabis inflorescence testing.
Posted on November 7, 2022
By LabLynx
Journal articles
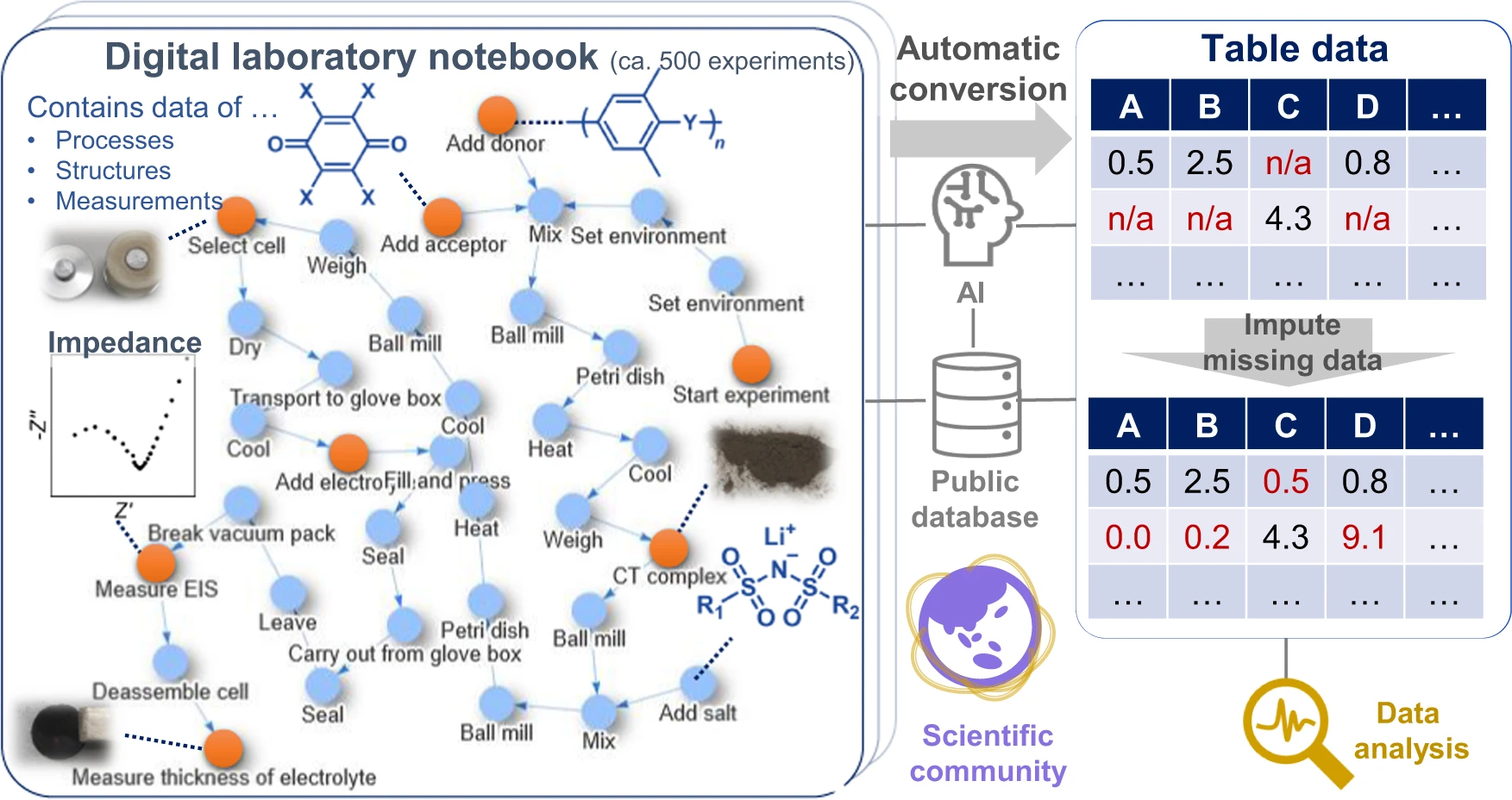
Like many other scientific disciplines, materials science is seeing many advances thanks to advanced computer systems that records large volumes of data and analyze it with speed. However, this data capture, analysis, and sharing has its challenges in material science, requiring more sophisticated systems. Hatakeyama-Sato
et al. highlight this fact with their materials informatics software platform that "losslessly describes the relationships of structures, properties, and processes as graphs in electronic laboratory notebooks (ELNs)." After describing the impetus for developing the platform, the authors explain its use within the context of materials informatics using a specific use case involving hundreds of experiments related to organic superionic glassy conductors. The authors include the methodology for those experiments and a wealth of supplementary information, while concluding their platform enables direct data sharing of material research, which "will improve scientific communication and accelerate integration of material knowledge."
Posted on October 31, 2022
By LabLynx
Journal articles
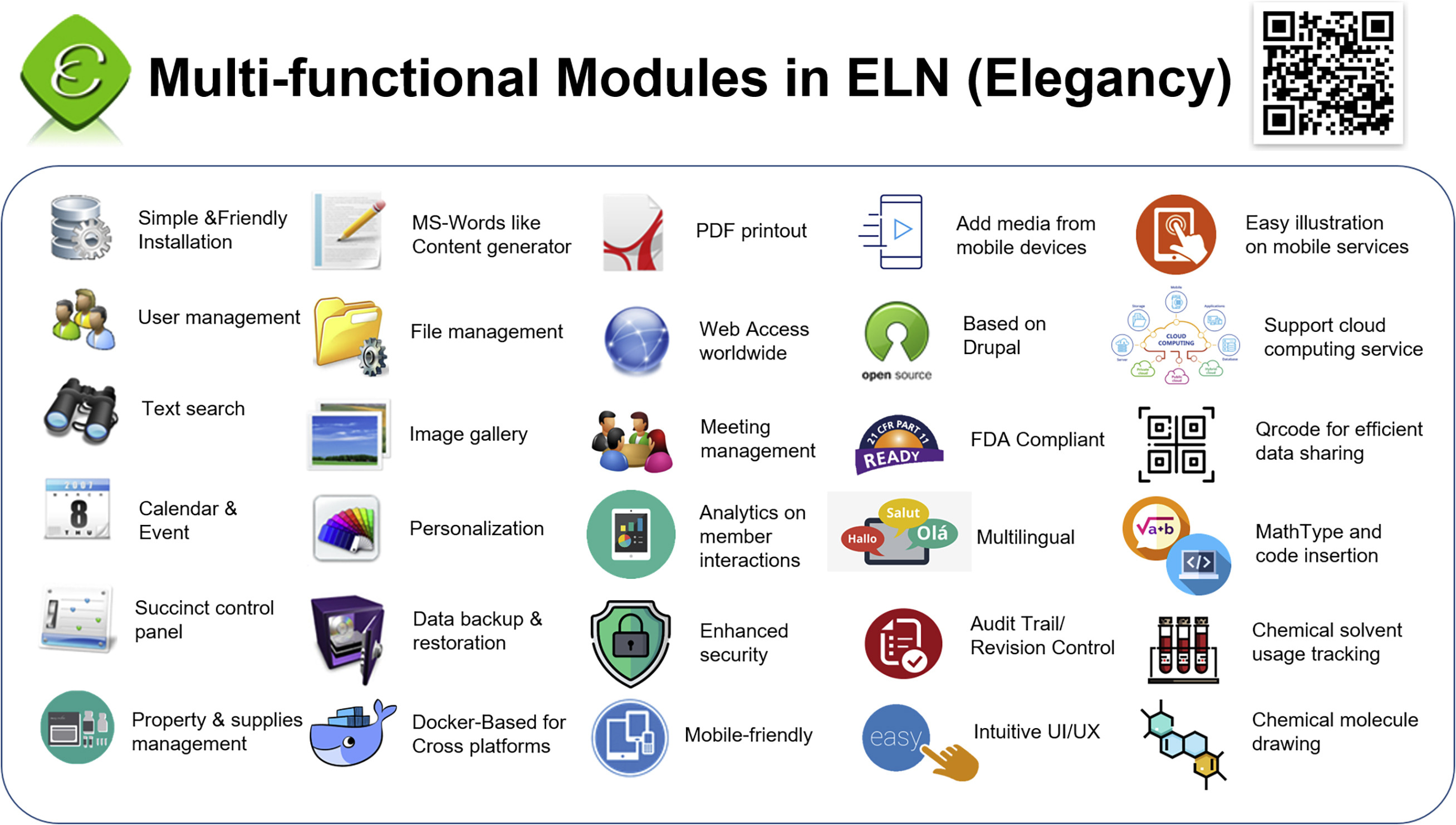
In this 2022 article published in the journal
iScience, Huang
et al. present their custom-made open-source electronic laboratory notebook (ELN) Elegancy. Citing insufficient functionality and ease of installation in free commercial and open-source options, the authors developed Elegancy, in part, using Drupal, PHP, and Docker, adding ELN features useful to most any lab, but also some features specifically useful to biomedical research labs. They describe the software's advantages and compare it to other similar options, highlighting Elegancy's easy no-code installation, data security, and biomedical and chemistry features. The authors close with discussion of its strengths and limitations, as well as related development details and software availability. The conclude that "Elegancy could help the scientific research community gather evidence, share information, reorganize knowledge, and digitize laboratory works with greater ease and security."
Posted on October 24, 2022
By LabLynx
Journal articles
In this short article published in the
Journal of the Medical Library Association, Foster, Whipple, and Rios describe their experiences and learnings from implementing an electronic laboratory notebook (ELN) at the Indiana University School of Medicine (IUSM). Known as the largest medical school in the US, IUSM has seen adoption of its chosen LabArchives ELN solution grow since early implementation in September 2018. After providing extensive background on the nature of ELNs and what they represent, the authors present their use case at IUSM and discuss the results, as well as the limitations inherent to their findings, within the scope of supporting ELN implementation through its libraries. They conclude that their work with ELNs "demonstrates the integral role libraries can have in supporting, growing, and shaping the information and data management priorities to move research reproducibility forward."
Posted on October 17, 2022
By LabLynx
Journal articles
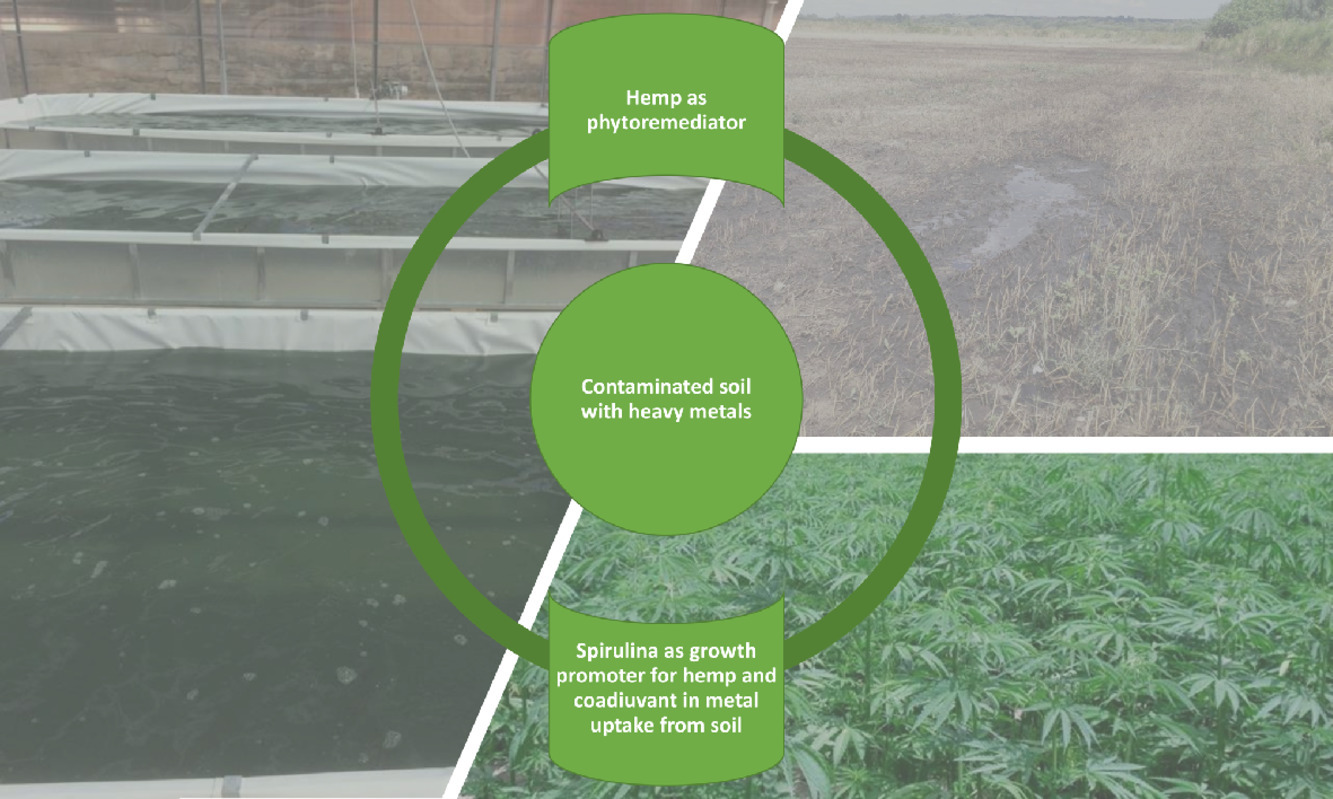
In this 2022 paper published in the journal
Environmental Advances, Musio
et al. explore the usefulness of
Cannabis sativa L. for the remediation of heavy metals from soils. While this concept is certainly not new, the authors also add the blue-green alga
Arthrospira platensis (spirulina) into the mix to see if further remediation gains can be made. Using nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy (NMR) and inductively coupled plasma atomic emission spectroscopy (ICP-AES) methods for analysis during the research, the authors come to several conclusions. First, they conclude that treatment of cannabis "with spirulina during the cultivation of the hemp induced an enhancement in the uptake of heavy metals." Second, they find that "NMR analysis allowed to identify the crucial variations of the metabolic composition that were induced by the treatment with spirulina," making it a useful analytical technique in this regard. By extension, they add, "the results described may encourage the application of spectroscopic methods for the rapid detection of structural changes in the various environmental spheres" and apply such remediation techniques in a monitored fashion.
Posted on October 10, 2022
By LabLynx
Journal articles
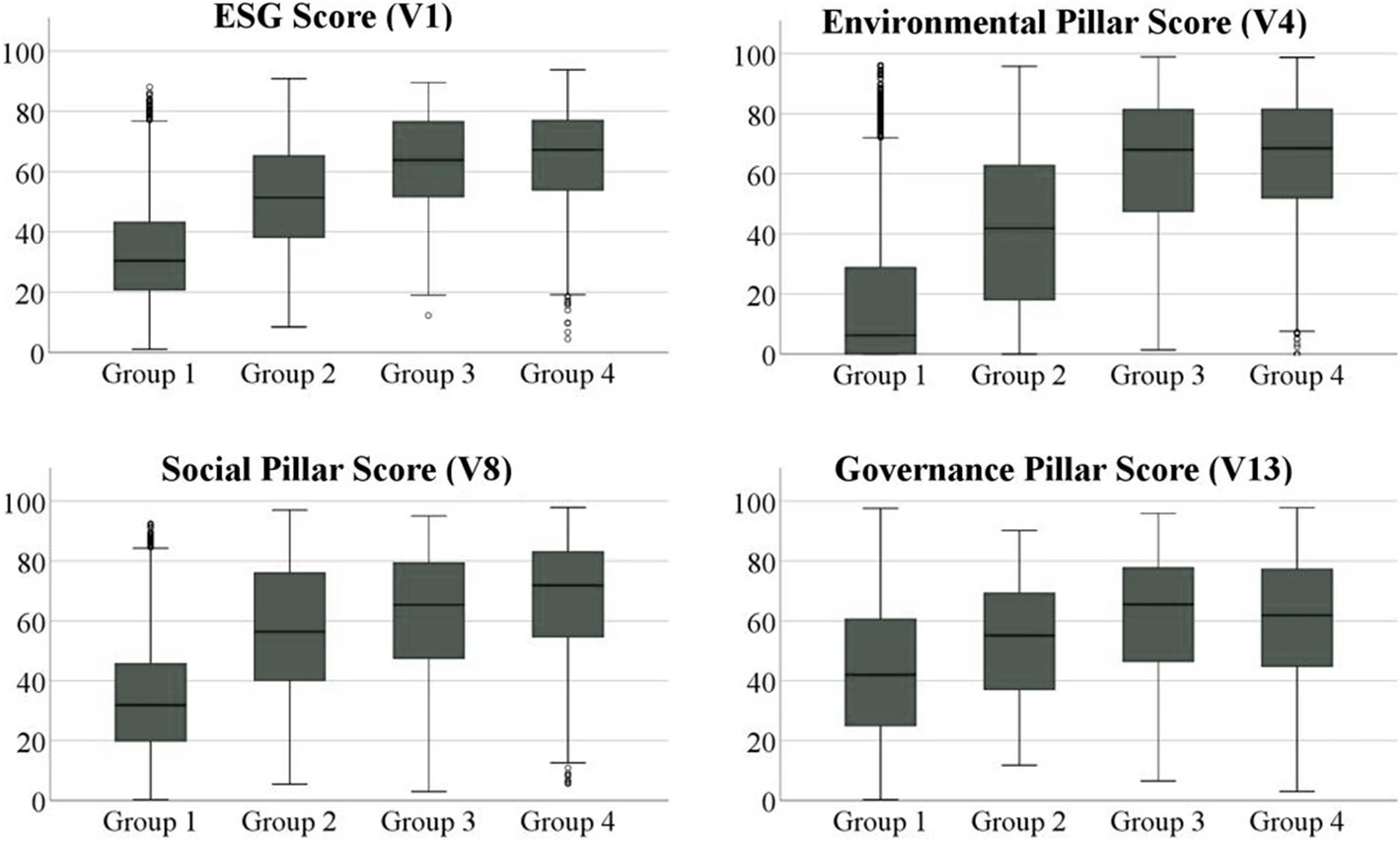
While this 2022 article published in
Environment, Development and Sustainability isn't directly about laboratories and informatics system, its discussion of quality management systems (QMSs) and environmental management systems (EMSs) remains highly relevant to the regulatory- and competition-driven laboratory of today. As Ronalter
et al. note, "growing societal and political focus on sustainability at the global level" places further pressure on businesses "to enhance their environmental, social, and governance (ESG) performance to satisfy respective stakeholder needs and ensure sustained business success"; laboratories and even laboratory software developers are not exempt from these pressures. The authors directly connect QMSs and EMSs to ESG performance in this paper, while highlighting "how combining these management systems can impact a corporation’s sustainable performance." Their study of ESG data is presented, and they conclude that adoption of such management systems "leads to positive developments" in workforce management, customer management, and supplier and stakeholder management, as well as in environmental efforts.
 In this 2022 paper published in the Egyptian Journal of Forensic Sciences, Prahladh and van Wyk provide a first-of-its-kind comprehensive scoping review of "articles involving unnatural deaths, focused on data practice or data management systems, relating to forensic medicine, all study designs, and published in English," with the goal of being able to draw conclusions about the current academic view of forensic data management. After examining more than 23,000 articles, the authors were only able to find 16 that met their criteria, according to their stated methodology. After a thorough review of those 16 articles, the duo concludes that "the literature shows that electronic data reporting systems are relevant and were developed from the recognition of coronial data as not only a part of the death investigation but as a contributor to preventable death research and public health initiatives." However, there are few lower- and middle-income countries (LMICs) represented in the study, and the authors believe that given how "forensic medicine departments can utilize simple and available tools that can advance standardization of data collection, storage, and reporting," it would behoove more LMICs to consider pilot systems such as "the Nigerian pilot program [that] still managed to contribute to statistically relevant data for impactful research" while using low-cost and readily available data management tools.
In this 2022 paper published in the Egyptian Journal of Forensic Sciences, Prahladh and van Wyk provide a first-of-its-kind comprehensive scoping review of "articles involving unnatural deaths, focused on data practice or data management systems, relating to forensic medicine, all study designs, and published in English," with the goal of being able to draw conclusions about the current academic view of forensic data management. After examining more than 23,000 articles, the authors were only able to find 16 that met their criteria, according to their stated methodology. After a thorough review of those 16 articles, the duo concludes that "the literature shows that electronic data reporting systems are relevant and were developed from the recognition of coronial data as not only a part of the death investigation but as a contributor to preventable death research and public health initiatives." However, there are few lower- and middle-income countries (LMICs) represented in the study, and the authors believe that given how "forensic medicine departments can utilize simple and available tools that can advance standardization of data collection, storage, and reporting," it would behoove more LMICs to consider pilot systems such as "the Nigerian pilot program [that] still managed to contribute to statistically relevant data for impactful research" while using low-cost and readily available data management tools.
 From disparate pools of data and information to inefficiencies in using that disparate data and information, the academic cancer center wishing to operate more effectively while improving patient outcomes and enabling more impactful research must turn to well-implemented data management systems and integrations. The University of Rochester Medical Center's James P. Wilmot Cancer Institute (WCI) was no exception to this greater need, turning to developing a custom data management platform called Hyperion to meet their needs. In this 2022 paper published in PLOS Digital Health, key stakeholders of Hyperion at WCI present the background on cancer center data management, as well as their methods in developing and results in using Hyperion. They follow this with discussion of their results, concluding that "Hyperion has surmounted large challenges in working with healthcare data to merge, organize, validate, and package data for use in multiple applications" at WCI, while also "lowering the skill floor for interaction with and maintenance of the software, reducing costs, and encouraging user autonomy." They add that a similar such system, from their viewpoint, could provide similar benefits in other academic cancer centers.
From disparate pools of data and information to inefficiencies in using that disparate data and information, the academic cancer center wishing to operate more effectively while improving patient outcomes and enabling more impactful research must turn to well-implemented data management systems and integrations. The University of Rochester Medical Center's James P. Wilmot Cancer Institute (WCI) was no exception to this greater need, turning to developing a custom data management platform called Hyperion to meet their needs. In this 2022 paper published in PLOS Digital Health, key stakeholders of Hyperion at WCI present the background on cancer center data management, as well as their methods in developing and results in using Hyperion. They follow this with discussion of their results, concluding that "Hyperion has surmounted large challenges in working with healthcare data to merge, organize, validate, and package data for use in multiple applications" at WCI, while also "lowering the skill floor for interaction with and maintenance of the software, reducing costs, and encouraging user autonomy." They add that a similar such system, from their viewpoint, could provide similar benefits in other academic cancer centers.
 In this 2022 journal article published in Metabolites, Djilali et al. present the results of a literature review "of studies performed on the effects of different storage conditions on the stability of cannabis compounds present in various biological matrices." Noting a growing need for accurate testing for the presence of cannabis compounds in humans, the authors first review the state of analysis among conventional biological matrices (i.e., blood, plasma, urine, and oral fluids) before looking at alternative matrices (i.e., breath, bile fluid, hair, sweat, cerumen, and dried blood spots). From their literature analysis, the authors made several conclusions about the various matrices, their collection methods, and their testing. Depending on the matrix, the authors recommended specific sample containers and storage temperatures among the conventional matrices, while noting that more research is required concerning laboratory testing of alternative matrices.
In this 2022 journal article published in Metabolites, Djilali et al. present the results of a literature review "of studies performed on the effects of different storage conditions on the stability of cannabis compounds present in various biological matrices." Noting a growing need for accurate testing for the presence of cannabis compounds in humans, the authors first review the state of analysis among conventional biological matrices (i.e., blood, plasma, urine, and oral fluids) before looking at alternative matrices (i.e., breath, bile fluid, hair, sweat, cerumen, and dried blood spots). From their literature analysis, the authors made several conclusions about the various matrices, their collection methods, and their testing. Depending on the matrix, the authors recommended specific sample containers and storage temperatures among the conventional matrices, while noting that more research is required concerning laboratory testing of alternative matrices.
 In this 2022 article published in the journal BMC Medical Ethics, Scheibner et al. present an assessment of Swiss hospital and medical research experts' views on using advanced technical solutions towards "sharing patient data in a privacy-preserving manner." In particular, the authors examine homomorphic encryption (HE) and distributed ledger technology (DLT) in the scope of European and Swiss regulatory frameworks. After an in-depth introduction on the topic, the authors present their methodology (an interview study) and their results, which touch upon five different information request scenarios. They then discuss the legal, ethical, and compatibility issues associated with using HE and DLT towards the problem of privacy-preserving patient data. They conclude that "a holistic approach needs to be taken to introducing HE and DLT as a mechanism for patient data management," one that tends "to recognize that social license and public trust from patients and physicians is as important as legal compliance."
In this 2022 article published in the journal BMC Medical Ethics, Scheibner et al. present an assessment of Swiss hospital and medical research experts' views on using advanced technical solutions towards "sharing patient data in a privacy-preserving manner." In particular, the authors examine homomorphic encryption (HE) and distributed ledger technology (DLT) in the scope of European and Swiss regulatory frameworks. After an in-depth introduction on the topic, the authors present their methodology (an interview study) and their results, which touch upon five different information request scenarios. They then discuss the legal, ethical, and compatibility issues associated with using HE and DLT towards the problem of privacy-preserving patient data. They conclude that "a holistic approach needs to be taken to introducing HE and DLT as a mechanism for patient data management," one that tends "to recognize that social license and public trust from patients and physicians is as important as legal compliance."
 This 2022 journal article published in AQUA - Water infrastructure, Ecosystems and Society sees Fernandes et al. presenting a computerized "system for reporting and learning from adverse events" in water sampling and analysis laboratories. The work was prompted by "a high frequency of adverse events in connection with sampling" at the Water Laboratory of Santiago do Cacém Municipality in Portugal. After introducing the topic of water quality testing and work related to using artificial intelligence (AI) in that testing, the authors describe their method of using a Eindhoven Classification Model (ECM) within the scope of ISO/IEC 17025 requirements. They then discuss the results of their software-based approach and conclude that their modular adverse event reporting and learning system has many strengths, particularly in that it "allows knowledge extraction, i.e., the identification of the main failure causes, possible trends, areas requiring improvement plans, or changes in procedures."
This 2022 journal article published in AQUA - Water infrastructure, Ecosystems and Society sees Fernandes et al. presenting a computerized "system for reporting and learning from adverse events" in water sampling and analysis laboratories. The work was prompted by "a high frequency of adverse events in connection with sampling" at the Water Laboratory of Santiago do Cacém Municipality in Portugal. After introducing the topic of water quality testing and work related to using artificial intelligence (AI) in that testing, the authors describe their method of using a Eindhoven Classification Model (ECM) within the scope of ISO/IEC 17025 requirements. They then discuss the results of their software-based approach and conclude that their modular adverse event reporting and learning system has many strengths, particularly in that it "allows knowledge extraction, i.e., the identification of the main failure causes, possible trends, areas requiring improvement plans, or changes in procedures."
 In this 2021 paper publisher in the journal Química Nova, Miguel et al. present the ISO/IEC 17025 standard in a historical context, while also providing some additional details about the concepts the standard proposes. As a quality management standard that also addresses competence, impartiality, and consistent operations in the laboratory, the standard emphasizes the importance of well-planned quality assurance towards reliable and traceable laboratory results. After an introduction to the standard, the authors take an in-depth look at ISO/IEC 17025's history and what drove changes to the standard over time. The article then examines what the standard asks of laboratories, as well as what value it adds to those labs. "By enacting ISO/IEC 17025," the authors conclude, "testing and calibration laboratories demonstrate they are responsible with their activities and their impacts, and put quality management and metrological traceability at the forefront of their operations."
In this 2021 paper publisher in the journal Química Nova, Miguel et al. present the ISO/IEC 17025 standard in a historical context, while also providing some additional details about the concepts the standard proposes. As a quality management standard that also addresses competence, impartiality, and consistent operations in the laboratory, the standard emphasizes the importance of well-planned quality assurance towards reliable and traceable laboratory results. After an introduction to the standard, the authors take an in-depth look at ISO/IEC 17025's history and what drove changes to the standard over time. The article then examines what the standard asks of laboratories, as well as what value it adds to those labs. "By enacting ISO/IEC 17025," the authors conclude, "testing and calibration laboratories demonstrate they are responsible with their activities and their impacts, and put quality management and metrological traceability at the forefront of their operations."
 Hemp? Cannabis? Marijuana? Industrial hemp? Salehi et al. note that terms like these and others are "a significant source of confusion for many," not just in the public but also within industry, marketing, and other groups. This not only causes issues with communicating research clearly but also employing that research to best effect. As such, the authors of this paper, published in the journal Frontiers in Pharmacology, pose the important question, "What is essential for defining Cannabis as a food, supplement, or drug?" Salehi et al. answer this question by reviewing a wide swath of current study on the Cannabis plant and its derivatives, highlighting critical definitions, composition, production practices, and pharmacological effects as part of defining the essentials of Cannabis. The authors also go into its use in foods, drugs, and supplements, as well as regulatory status and testing methodologies. They conclude that "despite all of the recent advances, several cannabis topics remain to be addressed," and addressing those topics will require more consistent terminology, greater understanding of the human endocannabinoid system, and a more consistent "platform for developing research about cannabis and related industries" within a number of countries.
Hemp? Cannabis? Marijuana? Industrial hemp? Salehi et al. note that terms like these and others are "a significant source of confusion for many," not just in the public but also within industry, marketing, and other groups. This not only causes issues with communicating research clearly but also employing that research to best effect. As such, the authors of this paper, published in the journal Frontiers in Pharmacology, pose the important question, "What is essential for defining Cannabis as a food, supplement, or drug?" Salehi et al. answer this question by reviewing a wide swath of current study on the Cannabis plant and its derivatives, highlighting critical definitions, composition, production practices, and pharmacological effects as part of defining the essentials of Cannabis. The authors also go into its use in foods, drugs, and supplements, as well as regulatory status and testing methodologies. They conclude that "despite all of the recent advances, several cannabis topics remain to be addressed," and addressing those topics will require more consistent terminology, greater understanding of the human endocannabinoid system, and a more consistent "platform for developing research about cannabis and related industries" within a number of countries.
 The quality management system (QMS) is increasingly a constant in laboratories of all types, lending support for better products and services coming out those labs. However, as technologies change and new challenges arise in research, medical, analytical, and R&D labs, the need for a more robust QMS becomes more obvious. In this 2022 article published in the journal Frontiers in Bioengineering and Biotechnology, Pillai et al. explore the varying frameworks of the QMS, which frameworks are best in which labs, and what implementation considerations should be made. After an informative introduction, the authors define the various laboratory types and match those types to the various QMS frameworks. They then provide a set of three critical recommendations for their implementation and use, concluding that while many frameworks are robust, the modern laboratory may need to incorporate more than one framework in order to fully achieve their quality goals. They add that "a holistic QMS framework complemented with guidance from multiple quality documents can benefit many laboratories that aim to address" the 12 quality system essentials (QSEs) of the Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute (CLSI).
The quality management system (QMS) is increasingly a constant in laboratories of all types, lending support for better products and services coming out those labs. However, as technologies change and new challenges arise in research, medical, analytical, and R&D labs, the need for a more robust QMS becomes more obvious. In this 2022 article published in the journal Frontiers in Bioengineering and Biotechnology, Pillai et al. explore the varying frameworks of the QMS, which frameworks are best in which labs, and what implementation considerations should be made. After an informative introduction, the authors define the various laboratory types and match those types to the various QMS frameworks. They then provide a set of three critical recommendations for their implementation and use, concluding that while many frameworks are robust, the modern laboratory may need to incorporate more than one framework in order to fully achieve their quality goals. They add that "a holistic QMS framework complemented with guidance from multiple quality documents can benefit many laboratories that aim to address" the 12 quality system essentials (QSEs) of the Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute (CLSI).
 In this 2022 article published in the journal Frontiers in Nutrition, Berciano et al. discuss the topic of precision or personalized nutrition (PN) in the context of needing advancements in analytical and data management technologies in order to reach its full potential. After a brief introduction and discussion of the concept of PN, the authors examine the role of big data and data analysis in PN, particularly in regards to developing and optimizing personalized nutrition products and services. They then couch PN in terms of it having the potential to be "the future of healthcare," addressing topics such as phenotyping, metabolic methods, environmental factors, and the role of money and medical service insurers. After compiling a set of best practices and standards in PN and addressing the need for advocacy efforts towards PN, the authors conclude that while "PN should have an impact on both personal and public health ... [a]dvancing the science and the adoption of PN will require a significant investment in multidisciplinary collaborations that translate the fast-moving technological advances in omics, sensors, AI, and big data management and analytics into powerful and user-friendly tools."
In this 2022 article published in the journal Frontiers in Nutrition, Berciano et al. discuss the topic of precision or personalized nutrition (PN) in the context of needing advancements in analytical and data management technologies in order to reach its full potential. After a brief introduction and discussion of the concept of PN, the authors examine the role of big data and data analysis in PN, particularly in regards to developing and optimizing personalized nutrition products and services. They then couch PN in terms of it having the potential to be "the future of healthcare," addressing topics such as phenotyping, metabolic methods, environmental factors, and the role of money and medical service insurers. After compiling a set of best practices and standards in PN and addressing the need for advocacy efforts towards PN, the authors conclude that while "PN should have an impact on both personal and public health ... [a]dvancing the science and the adoption of PN will require a significant investment in multidisciplinary collaborations that translate the fast-moving technological advances in omics, sensors, AI, and big data management and analytics into powerful and user-friendly tools."
 In this 2022 paper published in Talanta Open, Hall et al. propose an analytical method for 10 cannabis-related cannabinoids that is cost-efficient, rapid, and robust in its use. Noting "elevated cost and limited availability of certified analytical reference standards for some cannabinoids," the authors sought to develop a high-performance liquid chromatography-photodiode array (HPLC-PDA) method for 10 cannabinoids that uses "relative retention times (RRT) for peak identification and relative response factors (RRF) for their quantification." After describing their materials and methods, the authors present their results and discuss their implications towards various aspects such as accuracy, recovery, and quantification. They conclude that their method is robust, acceptably accurate, and has sufficient dynamic range. They add that with their method, "cost barriers for the analysis of panels of cannabinoids can be overcome, such that a diversity of cannabinoids can be analyzed as a part of routine quality control, with results that reflect the therapeutic efficacy for the consumer."
In this 2022 paper published in Talanta Open, Hall et al. propose an analytical method for 10 cannabis-related cannabinoids that is cost-efficient, rapid, and robust in its use. Noting "elevated cost and limited availability of certified analytical reference standards for some cannabinoids," the authors sought to develop a high-performance liquid chromatography-photodiode array (HPLC-PDA) method for 10 cannabinoids that uses "relative retention times (RRT) for peak identification and relative response factors (RRF) for their quantification." After describing their materials and methods, the authors present their results and discuss their implications towards various aspects such as accuracy, recovery, and quantification. They conclude that their method is robust, acceptably accurate, and has sufficient dynamic range. They add that with their method, "cost barriers for the analysis of panels of cannabinoids can be overcome, such that a diversity of cannabinoids can be analyzed as a part of routine quality control, with results that reflect the therapeutic efficacy for the consumer."
 In the age of "big data," appropriately implemented informatics solutions have become more important than ever. This has become particularly important to the world of cancer research and the weighty analyses of "the genome, epigenome, transcriptome, proteome, metabolome, and microbiome" of individuals. In this 2022 journal article by Hong et al., a review of the current state of cancer informatics is presented, addressing not only current informatics-supported applications but also challenges, opportunities, and future likelihoods. The authors conclude that not only "clinical oncology and research are reaping the benefits of informatics," but also that "with the further development of convenient and intelligent tools, informatics will enable earlier cancer detection, more precise cancer treatment, and better outcomes."
In the age of "big data," appropriately implemented informatics solutions have become more important than ever. This has become particularly important to the world of cancer research and the weighty analyses of "the genome, epigenome, transcriptome, proteome, metabolome, and microbiome" of individuals. In this 2022 journal article by Hong et al., a review of the current state of cancer informatics is presented, addressing not only current informatics-supported applications but also challenges, opportunities, and future likelihoods. The authors conclude that not only "clinical oncology and research are reaping the benefits of informatics," but also that "with the further development of convenient and intelligent tools, informatics will enable earlier cancer detection, more precise cancer treatment, and better outcomes."
 Interoperable health information systems in the United States has been a long-road effort that, according to Szarfman et al., has a long way to go yet to reach its full potential. Noting the strain on the digital health systems of hospitals, physician offices, laboratories, and other entities during the COVID-19 pandemic, the authors—many of them from the U.S. FDA—"recommend the implementation of standardized data collection and transmission systems, universal identifiers for individual patients and end users, a reference standard infrastructure to support calibration and integration of laboratory results from equivalent tests, and modernized working practices" in this brief paper. After providing a contextual introduction, they discuss the lack of universal and harmonized data collection and transmission standards and highlight five major issues with modern health systems that need immediate action. After briefly discussing return on investment in adopting the authors' recommendations, they conclude by posting 11 recommendations for U.S. legislators and nine recommendations for public-private partnerships in addressing the issues of health systems interoperability in the United States. They close by noting that while "this problem will not be cheap to fix ... it will be much costlier to ignore."
Interoperable health information systems in the United States has been a long-road effort that, according to Szarfman et al., has a long way to go yet to reach its full potential. Noting the strain on the digital health systems of hospitals, physician offices, laboratories, and other entities during the COVID-19 pandemic, the authors—many of them from the U.S. FDA—"recommend the implementation of standardized data collection and transmission systems, universal identifiers for individual patients and end users, a reference standard infrastructure to support calibration and integration of laboratory results from equivalent tests, and modernized working practices" in this brief paper. After providing a contextual introduction, they discuss the lack of universal and harmonized data collection and transmission standards and highlight five major issues with modern health systems that need immediate action. After briefly discussing return on investment in adopting the authors' recommendations, they conclude by posting 11 recommendations for U.S. legislators and nine recommendations for public-private partnerships in addressing the issues of health systems interoperability in the United States. They close by noting that while "this problem will not be cheap to fix ... it will be much costlier to ignore."
 In this 2022 paper published in Sensors, Henrichs et al. of the University of Hohenheim present their literature review on the topic of digital twins in the food and beverage industry. The concept of the digital twin—a digital representation of a product, process, or system that as closely as possible represents the characteristics of the physical representation—is relatively new, and its use in the food and beverage industry holds much promise, according to the authors' research. After an introduction and extensive background, the authors provide the methodology for their review, focusing on six critical questions. They then present their results from a broad perspective, and then a more in-depth discussion focusing on answering those six questions. They close by emphasizing related work in the field, and then concluding that while a majority of the research conducted by others involves the production and processing stages of food and beverage activities, a dearth of cases appear to discuss supply, processing, retail, and consumption. They also note that "relatively few focus on the integration of digital twins in systems for developing autonomous control or providing recommendations to humans," which could be practically useful in the industry. "Nevertheless, digital twins provide huge potentials," they add, "e.g., in determining food quality, ensuring traceability, or designing personalized foods."
In this 2022 paper published in Sensors, Henrichs et al. of the University of Hohenheim present their literature review on the topic of digital twins in the food and beverage industry. The concept of the digital twin—a digital representation of a product, process, or system that as closely as possible represents the characteristics of the physical representation—is relatively new, and its use in the food and beverage industry holds much promise, according to the authors' research. After an introduction and extensive background, the authors provide the methodology for their review, focusing on six critical questions. They then present their results from a broad perspective, and then a more in-depth discussion focusing on answering those six questions. They close by emphasizing related work in the field, and then concluding that while a majority of the research conducted by others involves the production and processing stages of food and beverage activities, a dearth of cases appear to discuss supply, processing, retail, and consumption. They also note that "relatively few focus on the integration of digital twins in systems for developing autonomous control or providing recommendations to humans," which could be practically useful in the industry. "Nevertheless, digital twins provide huge potentials," they add, "e.g., in determining food quality, ensuring traceability, or designing personalized foods."
 In this 2022 journal article published in Advances in Sample Preparation, Capetti et al. of Università di Torino investigate the advantages and disadvantages that vacuum-assisted headspace solid-phase microextraction (Vac-HSSPME) may lend to the process of Cannabis inflorescence preparation and subsequent testing, by gas chromatography–mass spectrometry (GC-MS), in order to accurately characterize both terpenoid and cannabinoid profiles. After providing an introduction on the topic, the authors describe the materials and methods used, as well as the results of their study. They conclude that "compared to standard HSSPME, vacuum conditions in the headspace ensure the fast recovery of cannabinoid markers at considerably lower sampling temperature (i.e., 90°C) that do not discriminate the most volatile fraction nor cause the formation of artifacts when the sampling time is minimized." They add that, in combination with GC-MS, Vac-HSSPME can prove to be "fast, totally automatable, and solvent-free," representing a more green analytical approach to Cannabis inflorescence testing.
In this 2022 journal article published in Advances in Sample Preparation, Capetti et al. of Università di Torino investigate the advantages and disadvantages that vacuum-assisted headspace solid-phase microextraction (Vac-HSSPME) may lend to the process of Cannabis inflorescence preparation and subsequent testing, by gas chromatography–mass spectrometry (GC-MS), in order to accurately characterize both terpenoid and cannabinoid profiles. After providing an introduction on the topic, the authors describe the materials and methods used, as well as the results of their study. They conclude that "compared to standard HSSPME, vacuum conditions in the headspace ensure the fast recovery of cannabinoid markers at considerably lower sampling temperature (i.e., 90°C) that do not discriminate the most volatile fraction nor cause the formation of artifacts when the sampling time is minimized." They add that, in combination with GC-MS, Vac-HSSPME can prove to be "fast, totally automatable, and solvent-free," representing a more green analytical approach to Cannabis inflorescence testing.
 Like many other scientific disciplines, materials science is seeing many advances thanks to advanced computer systems that records large volumes of data and analyze it with speed. However, this data capture, analysis, and sharing has its challenges in material science, requiring more sophisticated systems. Hatakeyama-Sato et al. highlight this fact with their materials informatics software platform that "losslessly describes the relationships of structures, properties, and processes as graphs in electronic laboratory notebooks (ELNs)." After describing the impetus for developing the platform, the authors explain its use within the context of materials informatics using a specific use case involving hundreds of experiments related to organic superionic glassy conductors. The authors include the methodology for those experiments and a wealth of supplementary information, while concluding their platform enables direct data sharing of material research, which "will improve scientific communication and accelerate integration of material knowledge."
Like many other scientific disciplines, materials science is seeing many advances thanks to advanced computer systems that records large volumes of data and analyze it with speed. However, this data capture, analysis, and sharing has its challenges in material science, requiring more sophisticated systems. Hatakeyama-Sato et al. highlight this fact with their materials informatics software platform that "losslessly describes the relationships of structures, properties, and processes as graphs in electronic laboratory notebooks (ELNs)." After describing the impetus for developing the platform, the authors explain its use within the context of materials informatics using a specific use case involving hundreds of experiments related to organic superionic glassy conductors. The authors include the methodology for those experiments and a wealth of supplementary information, while concluding their platform enables direct data sharing of material research, which "will improve scientific communication and accelerate integration of material knowledge."
 In this 2022 article published in the journal iScience, Huang et al. present their custom-made open-source electronic laboratory notebook (ELN) Elegancy. Citing insufficient functionality and ease of installation in free commercial and open-source options, the authors developed Elegancy, in part, using Drupal, PHP, and Docker, adding ELN features useful to most any lab, but also some features specifically useful to biomedical research labs. They describe the software's advantages and compare it to other similar options, highlighting Elegancy's easy no-code installation, data security, and biomedical and chemistry features. The authors close with discussion of its strengths and limitations, as well as related development details and software availability. The conclude that "Elegancy could help the scientific research community gather evidence, share information, reorganize knowledge, and digitize laboratory works with greater ease and security."
In this 2022 article published in the journal iScience, Huang et al. present their custom-made open-source electronic laboratory notebook (ELN) Elegancy. Citing insufficient functionality and ease of installation in free commercial and open-source options, the authors developed Elegancy, in part, using Drupal, PHP, and Docker, adding ELN features useful to most any lab, but also some features specifically useful to biomedical research labs. They describe the software's advantages and compare it to other similar options, highlighting Elegancy's easy no-code installation, data security, and biomedical and chemistry features. The authors close with discussion of its strengths and limitations, as well as related development details and software availability. The conclude that "Elegancy could help the scientific research community gather evidence, share information, reorganize knowledge, and digitize laboratory works with greater ease and security."
 In this short article published in the Journal of the Medical Library Association, Foster, Whipple, and Rios describe their experiences and learnings from implementing an electronic laboratory notebook (ELN) at the Indiana University School of Medicine (IUSM). Known as the largest medical school in the US, IUSM has seen adoption of its chosen LabArchives ELN solution grow since early implementation in September 2018. After providing extensive background on the nature of ELNs and what they represent, the authors present their use case at IUSM and discuss the results, as well as the limitations inherent to their findings, within the scope of supporting ELN implementation through its libraries. They conclude that their work with ELNs "demonstrates the integral role libraries can have in supporting, growing, and shaping the information and data management priorities to move research reproducibility forward."
In this short article published in the Journal of the Medical Library Association, Foster, Whipple, and Rios describe their experiences and learnings from implementing an electronic laboratory notebook (ELN) at the Indiana University School of Medicine (IUSM). Known as the largest medical school in the US, IUSM has seen adoption of its chosen LabArchives ELN solution grow since early implementation in September 2018. After providing extensive background on the nature of ELNs and what they represent, the authors present their use case at IUSM and discuss the results, as well as the limitations inherent to their findings, within the scope of supporting ELN implementation through its libraries. They conclude that their work with ELNs "demonstrates the integral role libraries can have in supporting, growing, and shaping the information and data management priorities to move research reproducibility forward."
 In this 2022 paper published in the journal Environmental Advances, Musio et al. explore the usefulness of Cannabis sativa L. for the remediation of heavy metals from soils. While this concept is certainly not new, the authors also add the blue-green alga Arthrospira platensis (spirulina) into the mix to see if further remediation gains can be made. Using nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy (NMR) and inductively coupled plasma atomic emission spectroscopy (ICP-AES) methods for analysis during the research, the authors come to several conclusions. First, they conclude that treatment of cannabis "with spirulina during the cultivation of the hemp induced an enhancement in the uptake of heavy metals." Second, they find that "NMR analysis allowed to identify the crucial variations of the metabolic composition that were induced by the treatment with spirulina," making it a useful analytical technique in this regard. By extension, they add, "the results described may encourage the application of spectroscopic methods for the rapid detection of structural changes in the various environmental spheres" and apply such remediation techniques in a monitored fashion.
In this 2022 paper published in the journal Environmental Advances, Musio et al. explore the usefulness of Cannabis sativa L. for the remediation of heavy metals from soils. While this concept is certainly not new, the authors also add the blue-green alga Arthrospira platensis (spirulina) into the mix to see if further remediation gains can be made. Using nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy (NMR) and inductively coupled plasma atomic emission spectroscopy (ICP-AES) methods for analysis during the research, the authors come to several conclusions. First, they conclude that treatment of cannabis "with spirulina during the cultivation of the hemp induced an enhancement in the uptake of heavy metals." Second, they find that "NMR analysis allowed to identify the crucial variations of the metabolic composition that were induced by the treatment with spirulina," making it a useful analytical technique in this regard. By extension, they add, "the results described may encourage the application of spectroscopic methods for the rapid detection of structural changes in the various environmental spheres" and apply such remediation techniques in a monitored fashion.
 While this 2022 article published in Environment, Development and Sustainability isn't directly about laboratories and informatics system, its discussion of quality management systems (QMSs) and environmental management systems (EMSs) remains highly relevant to the regulatory- and competition-driven laboratory of today. As Ronalter et al. note, "growing societal and political focus on sustainability at the global level" places further pressure on businesses "to enhance their environmental, social, and governance (ESG) performance to satisfy respective stakeholder needs and ensure sustained business success"; laboratories and even laboratory software developers are not exempt from these pressures. The authors directly connect QMSs and EMSs to ESG performance in this paper, while highlighting "how combining these management systems can impact a corporation’s sustainable performance." Their study of ESG data is presented, and they conclude that adoption of such management systems "leads to positive developments" in workforce management, customer management, and supplier and stakeholder management, as well as in environmental efforts.
While this 2022 article published in Environment, Development and Sustainability isn't directly about laboratories and informatics system, its discussion of quality management systems (QMSs) and environmental management systems (EMSs) remains highly relevant to the regulatory- and competition-driven laboratory of today. As Ronalter et al. note, "growing societal and political focus on sustainability at the global level" places further pressure on businesses "to enhance their environmental, social, and governance (ESG) performance to satisfy respective stakeholder needs and ensure sustained business success"; laboratories and even laboratory software developers are not exempt from these pressures. The authors directly connect QMSs and EMSs to ESG performance in this paper, while highlighting "how combining these management systems can impact a corporation’s sustainable performance." Their study of ESG data is presented, and they conclude that adoption of such management systems "leads to positive developments" in workforce management, customer management, and supplier and stakeholder management, as well as in environmental efforts.
















